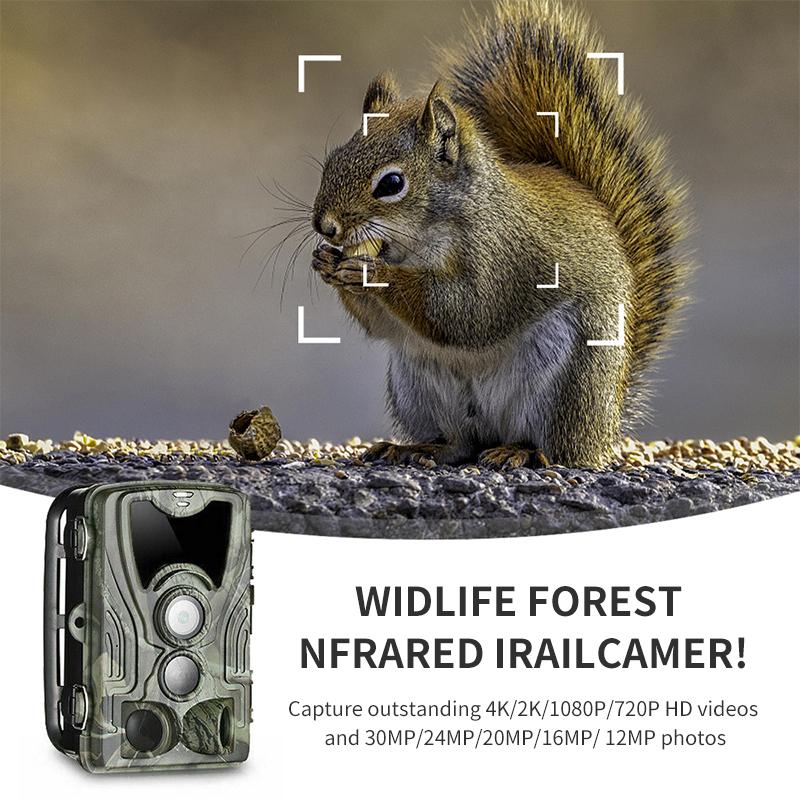
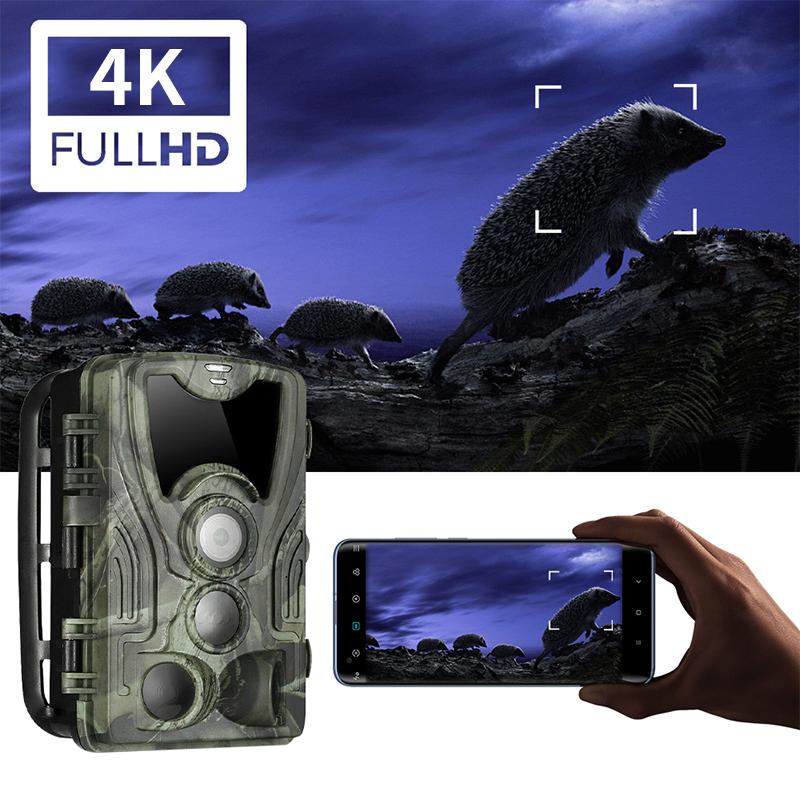
Camera Settings When Wifi Protected?
Camera Settings for Optimal Performance When Using Wi-Fi Protection
In today's connected world, wireless networks have revolutionized how we interact with our devices, including cameras. From security systems to professional photography tools and even everyday smartphones, the convenience of Wi-Fi connectivity allows us to easily transfer files, control cameras remotely, and even stream videos. However, ensuring that your camera works effectively and securely over Wi-Fi requires understanding and configuring several settings correctly. This article delves into the best camera settings to use when Wi-Fi protection is a necessity, ensuring both optimal performance and security.
Understanding Wi-Fi Protection

Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and its more advanced versions WPA2 and WPA3 are designed to secure wireless networks by encrypting data and ensuring only authorized devices can connect. For cameras, these protocols ensure that photos, videos, and live feeds are not accessible to unauthorized users.
Why Camera Settings Matter

Configuring your camera settings is vital for securing data, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring smooth connectivity and functionality. Proper settings can help avoid issues such as lag, interference, and quality degradation, which are pivotal for applications ranging from casual photography to critical security monitoring.
Core Camera Settings for Wi-Fi Protection

1. Wi-Fi Network Configuration
Ensure your camera is connected to a secure network using WPA2 or WPA3 encryption. Avoid using WEP or open networks as they are highly vulnerable to unauthorized access.
- SSID Visibility: Consider hiding your network's SSID (Service Set Identifier) to make it less detectable to unauthorized users.
- Password Strength: Use a strong, complex password for your Wi-Fi network to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Firmware and Software Updates
Keeping your camera's firmware and any associated software up-to-date ensures that you have the latest security patches and performance improvements. Manufacturers frequently release updates to address new vulnerabilities and enhance device functionality.
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates if the option is available, or routinely check for updates manually.
3. Encryption Settings
Enable encryption for data transmission between the camera and your device. This ensures that even if data were intercepted, it would be difficult for the unauthorized user to decipher it.
- End-to-End Encryption: Opt for end-to-end encryption where possible. This means that data is encrypted on your camera and only decrypted on your receiving device.
4. Network Band Settings
Choose the appropriate frequency band (2.4GHz or 5GHz) for your camera's Wi-Fi connection. Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
- 2.4GHz: Offers a longer range but is susceptible to interference from other wireless devices and has lower data speeds.
- 5GHz: Provides higher data speeds and reduced interference but with a shorter range. It's better for high-bandwidth activities like streaming video.
5. Quality of Service (QoS)
Configure Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router to prioritize traffic from your camera. This helps to ensure smooth and uninterrupted streaming or file transfers, crucial for both security cameras and live-event recordings.
- Bandwidth Allocation: Allocate sufficient bandwidth to the camera to prevent video lag or buffer issues.
- Traffic Priority: Mark the camera’s data packets with high priority.
6. Remote Access Settings
If you need to access your camera remotely, ensure that remote access features are secure.
- VPN Usage: Utilize a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for remote access to add an additional layer of security.
- Port Forwarding: Use secure, non-standard ports for remote access and disable UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) to prevent automatic port forwarding.
Mitigating Risks and Troubleshooting

Implementing the above settings enhances security but also may introduce challenges such as connectivity issues or reduced performance. Here are some tips to mitigate such risks:
1. Signal Interference: If you experience interference, changing the broadcasting channel on your router can significantly improve connectivity.
2. Bandwidth Management: Monitor and manage the bandwidth usage of all connected devices to ensure your camera gets the necessary share for optimal performance.
3. Firewall Configuration: Ensure that your firewall settings are not overly restrictive, allowing essential traffic from your camera but blocking suspicious activity.
4. Regular Reboots: Periodically reboot your router and camera to clear any potential issues and apply new settings effectively.
Advanced Tips for Professional Use
For professional photographers and security providers, additional considerations may optimize performance further:
1. Static IP Address: Assign a static IP address to your camera to prevent connection issues that can arise with dynamic IP addresses.
2. Dual-band Routers: Utilize dual-band routers that support both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands for greater flexibility and performance.
3. NAS Integration: Configure your camera to work with Network Attached Storage (NAS) for robust, secure storage options.
Understanding and configuring camera settings for Wi-Fi protection is an essential task to ensure both performance and security. By employing strong encryption, keeping software updated, configuring network bands properly, and managing both local and remote access securely, you can greatly enhance the safety and efficiency of your camera systems. Whether you're a casual user or a professional, the right settings make a significant difference in protecting your assets and ensuring smooth, uninterrupted functionality. Always stay informed about the latest security protocols and technological advancements to keep your systems in optimal condition.








































There are no comments for this blog.