How Camera Detector Works?
In today's world, privacy and security are paramount concerns for individuals and organizations alike. With the proliferation of hidden cameras, the need for effective camera detection technology has become increasingly important. This article delves into the workings of camera detectors, exploring the various technologies and methods used to identify hidden cameras, and providing practical advice on how to use these devices effectively.
Understanding Camera Detectors

Camera detectors are devices designed to identify the presence of hidden cameras in a given area. These detectors can be used in various settings, including homes, offices, hotels, and public spaces, to ensure privacy and security. The primary function of a camera detector is to locate hidden cameras, which can be disguised as everyday objects such as smoke detectors, clocks, or even electrical outlets.
Types of Camera Detectors

There are several types of camera detectors, each utilizing different technologies to identify hidden cameras. The most common types include:
1. RF (Radio Frequency) Detectors: These devices detect the radio frequency signals emitted by wireless cameras. When a hidden camera transmits video or audio signals, it generates RF signals that can be picked up by an RF detector. These detectors are effective for identifying wireless cameras but may not be as useful for detecting wired cameras or cameras that are not actively transmitting.
2. Lens Detectors: Lens detectors use optical technology to identify the reflective surfaces of camera lenses. These devices typically emit a beam of light, which reflects off the lens of a hidden camera, making it visible to the user. Lens detectors are effective for locating both wired and wireless cameras, as well as cameras that are not actively transmitting.
3. Infrared (IR) Detectors: Infrared detectors identify the infrared light emitted by night-vision cameras. These cameras use IR light to capture images in low-light conditions, and IR detectors can pick up this light, revealing the presence of a hidden camera. IR detectors are particularly useful for identifying cameras that operate in the dark.
4. Combination Detectors: Some camera detectors combine multiple detection technologies, such as RF, lens, and IR detection, to provide a more comprehensive solution. These combination detectors are often more effective at identifying hidden cameras, as they can detect a wider range of camera types and technologies.
How Camera Detectors Work

The operation of a camera detector depends on the type of technology it uses. Here is a detailed explanation of how each type of camera detector works:
1. RF Detectors: RF detectors scan the surrounding area for radio frequency signals. When a wireless camera transmits video or audio, it generates RF signals within a specific frequency range. The RF detector picks up these signals and alerts the user to the presence of a hidden camera. Some RF detectors can also display the strength of the signal, helping the user pinpoint the exact location of the camera.
2. Lens Detectors: Lens detectors emit a beam of light, often in the form of a laser or LED. When this light hits the lens of a hidden camera, it reflects back to the detector, creating a visible glint or flash. The user can then identify the location of the hidden camera by looking for this reflection. Some lens detectors also use filters to enhance the visibility of the reflected light, making it easier to spot hidden cameras.
3. IR Detectors: Infrared detectors work by identifying the infrared light emitted by night-vision cameras. These detectors typically use IR sensors to pick up the IR light, which is invisible to the human eye. When the detector senses IR light, it alerts the user to the presence of a hidden camera. Some IR detectors also include visual displays that show the location of the IR light source, helping the user locate the hidden camera more easily.
4. Combination Detectors: Combination detectors incorporate multiple detection technologies to provide a more comprehensive solution. These devices can scan for RF signals, detect lens reflections, and identify IR light, making them more effective at locating hidden cameras. By using multiple detection methods, combination detectors can identify a wider range of camera types and technologies, increasing the likelihood of finding hidden cameras.
Practical Tips for Using Camera Detectors
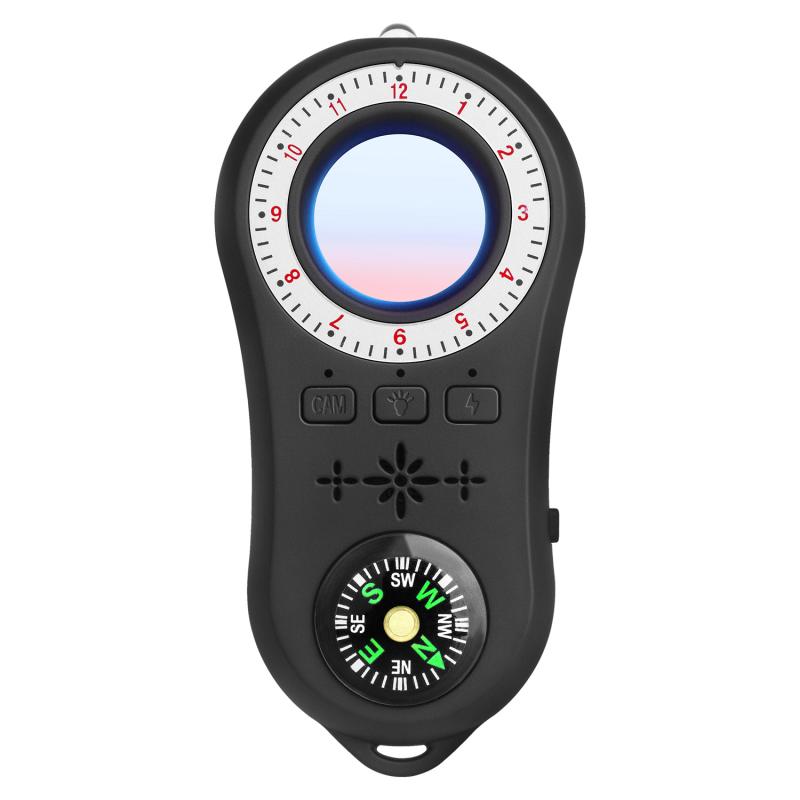

To effectively use a camera detector, follow these practical tips:
1. Conduct a Thorough Sweep: When using a camera detector, it is essential to conduct a thorough sweep of the area. Move the detector slowly and methodically, covering all possible hiding spots, including ceilings, walls, furniture, and everyday objects. Pay special attention to areas where hidden cameras are commonly placed, such as smoke detectors, clocks, and electrical outlets.
2. Check for Multiple Camera Types: Since hidden cameras can use different technologies, it is important to check for multiple camera types. Use a combination detector or multiple detectors to scan for RF signals, lens reflections, and IR light. This approach increases the likelihood of identifying all hidden cameras in the area.
3. Be Aware of False Positives: Camera detectors can sometimes produce false positives, detecting signals or reflections from non-camera sources. To minimize false positives, familiarize yourself with the normal RF signals and reflective surfaces in the area. If the detector alerts you to a potential hidden camera, investigate further to confirm its presence.
4. Regularly Update Your Equipment: As camera technology evolves, so do the methods for hiding cameras. Regularly update your camera detection equipment to ensure it can identify the latest camera technologies. Newer detectors may offer improved sensitivity, better detection ranges, and additional features that enhance their effectiveness.
5. Use in Conjunction with Other Security Measures: Camera detectors are an important tool for ensuring privacy and security, but they should be used in conjunction with other security measures. Implementing physical security measures, such as locks and access controls, can help prevent unauthorized access and the placement of hidden cameras. Additionally, educating employees and family members about the risks of hidden cameras and how to identify them can further enhance security.
Camera detectors play a crucial role in protecting privacy and security in various settings. By understanding how these devices work and following practical tips for their use, individuals and organizations can effectively identify and mitigate the risks posed by hidden cameras. Whether using RF detectors, lens detectors, IR detectors, or combination detectors, a comprehensive approach to camera detection can help ensure a safe and secure environment. Regularly updating detection equipment and combining camera detectors with other security measures can further enhance the effectiveness of privacy protection efforts.