How Camera Gimbal Works?
In the world of photography and videography, achieving smooth, stable shots is a constant challenge. Whether you're a professional filmmaker or an enthusiastic hobbyist, the quest for that perfect, shake-free footage is universal. Enter the camera gimbal—a revolutionary tool that has transformed the way we capture motion. But how exactly does a camera gimbal work? In this article, we'll delve into the mechanics, technology, and practical applications of camera gimbals, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential piece of equipment.
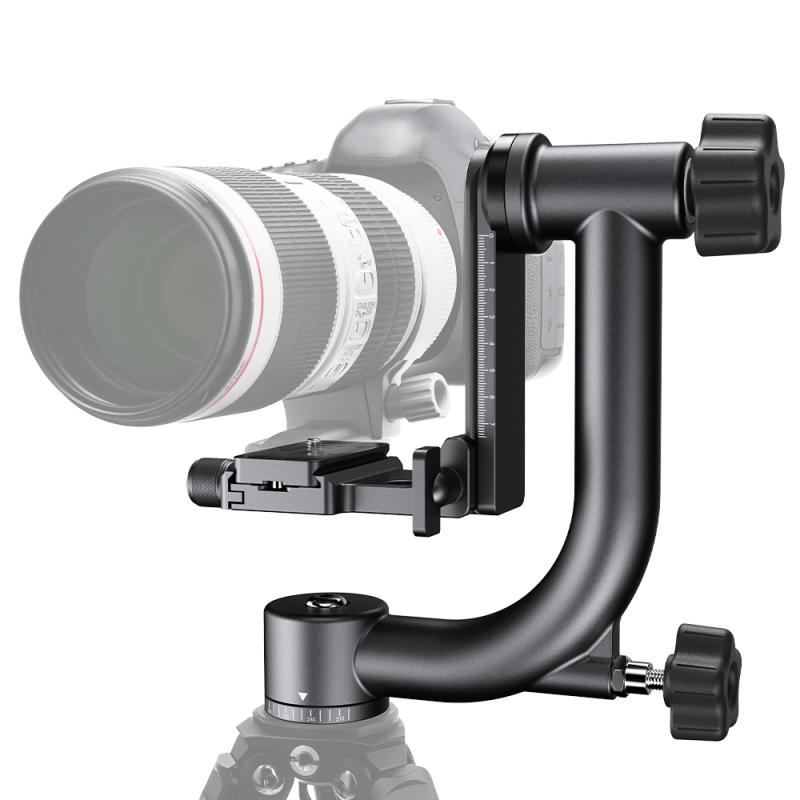

Understanding the Basics of Camera Gimbals
A camera gimbal is a pivoted support that allows the rotation of an object about a single axis. In the context of photography and videography, a gimbal stabilizes the camera, allowing for smooth, fluid motion. The primary function of a gimbal is to counteract unwanted movements, such as shaking or tilting, which can occur when the camera is handheld or mounted on a moving platform.
The Core Components of a Camera Gimbal
To understand how a camera gimbal works, it's essential to familiarize yourself with its core components:
1. Motors: Modern gimbals typically use brushless motors to control the movement of the camera. These motors are responsible for stabilizing the camera by counteracting any unwanted motion.
2. Sensors: Gimbals are equipped with various sensors, including accelerometers and gyroscopes, which detect the camera's orientation and movement. These sensors provide real-time data to the gimbal's control system.
3. Control System: The control system, often a microcontroller, processes the data from the sensors and sends commands to the motors to adjust the camera's position. This system ensures that the camera remains stable and level, regardless of external movements.
4. Mounting Platform: The camera is mounted on a platform that is connected to the gimbal's motors. This platform can move independently of the gimbal's base, allowing for smooth, stabilized shots.
The Working Principle of a Camera Gimbal

The working principle of a camera gimbal revolves around the concept of stabilization through counteractive motion. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
1. Detection of Movement: The sensors on the gimbal continuously monitor the camera's orientation and movement. For instance, if the camera tilts to the left, the sensors detect this change in position.
2. Data Processing: The control system receives the data from the sensors and processes it to determine the necessary adjustments. This involves calculating the degree and direction of the unwanted movement.
3. Motor Activation: Based on the processed data, the control system sends commands to the brushless motors. These motors then move the mounting platform in the opposite direction of the detected movement. For example, if the camera tilts to the left, the motors will tilt the platform to the right to counteract the motion.
4. Stabilization: The counteractive motion of the motors stabilizes the camera, ensuring that it remains level and steady. This process happens in real-time, allowing for smooth, fluid shots even in dynamic environments.
Types of Camera Gimbals
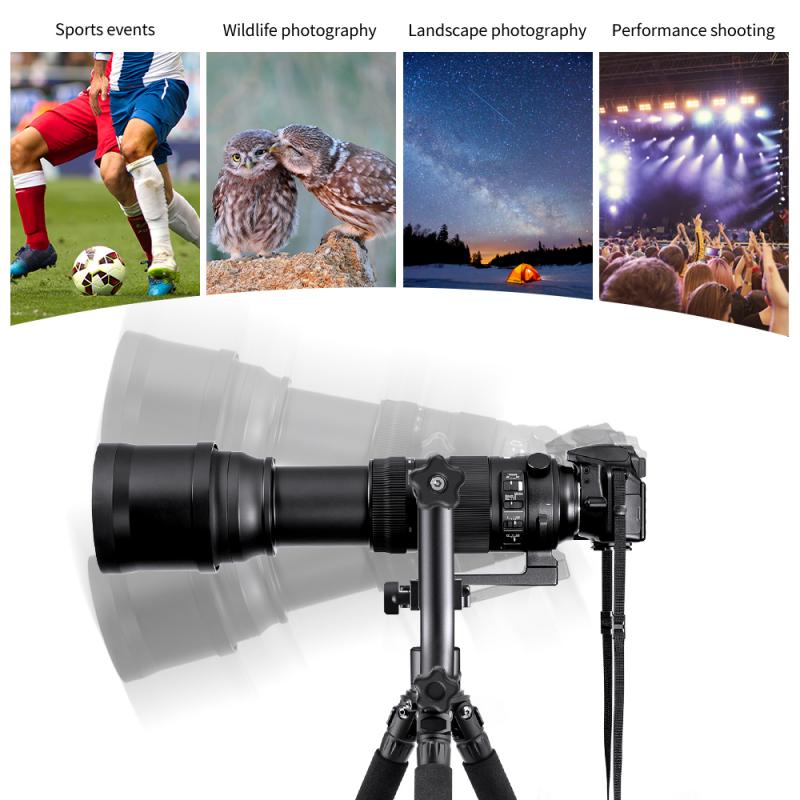

Camera gimbals come in various types, each designed for specific applications and camera setups. The most common types include:
1. Handheld Gimbals: These are portable gimbals designed for use with smartphones, action cameras, and small DSLRs or mirrorless cameras. Handheld gimbals are popular among vloggers, travel photographers, and hobbyists due to their ease of use and portability.
2. Wearable Gimbals: Wearable gimbals are designed to be mounted on the body or equipment, such as helmets or chest rigs. They are commonly used in action sports and adventure filming to capture dynamic, first-person perspectives.
3. Aerial Gimbals: Aerial gimbals are used with drones to stabilize cameras during flight. These gimbals are crucial for capturing smooth aerial footage, as they counteract the vibrations and movements of the drone.
4. Vehicle-Mounted Gimbals: These gimbals are mounted on vehicles, such as cars or boats, to stabilize cameras during high-speed or rough-terrain filming. They are often used in professional filmmaking and documentary production.
Practical Applications of Camera Gimbals
Camera gimbals have a wide range of practical applications, making them indispensable tools in various fields:
1. Filmmaking: In the film industry, gimbals are used to achieve smooth, cinematic shots. They allow filmmakers to capture complex movements and dynamic scenes without the need for bulky equipment like dollies or cranes.
2. Vlogging and Content Creation: For vloggers and content creators, handheld gimbals provide a convenient way to capture high-quality, stable footage on the go. This is especially useful for travel vlogs, live streaming, and social media content.
3. Sports and Action Filming: Wearable and handheld gimbals are popular in sports and action filming, where capturing fast-paced, dynamic movements is essential. Gimbals ensure that the footage remains smooth and watchable, even in extreme conditions.
4. Aerial Photography and Videography: Aerial gimbals are crucial for drone operators, enabling them to capture stunning, stable footage from the sky. This is particularly valuable in real estate, landscape photography, and cinematography.
5. Documentary Production: In documentary filmmaking, gimbals allow for fluid, unobtrusive camera movements. This is important for capturing natural, candid moments without disrupting the scene.
Tips for Using a Camera Gimbal
To get the most out of your camera gimbal, consider the following tips:
1. Balance Your Camera: Properly balancing your camera on the gimbal is crucial for optimal performance. Follow the manufacturer's instructions to ensure that the camera is correctly positioned and balanced.
2. Calibrate the Gimbal: Regularly calibrate your gimbal to ensure that the sensors and motors are functioning correctly. This helps maintain accurate stabilization and prevents drift.
3. Practice Smooth Movements: While the gimbal stabilizes the camera, your movements also play a role in achieving smooth shots. Practice gentle, fluid movements to complement the gimbal's stabilization.
4. Use the Right Mode: Many gimbals offer different modes, such as follow mode, lock mode, and pan mode. Experiment with these modes to find the best settings for your shooting style and environment.
5. Monitor Battery Life: Gimbals rely on battery power to operate the motors and sensors. Keep an eye on the battery life and carry spare batteries if needed to avoid interruptions during shooting.
Camera gimbals have revolutionized the way we capture motion, providing filmmakers, photographers, and content creators with the tools to achieve smooth, stable shots in a variety of environments. By understanding the mechanics and technology behind gimbals, you can make informed decisions about which type of gimbal best suits your needs and how to use it effectively. Whether you're shooting a high-speed action sequence, a serene landscape, or a candid documentary, a camera gimbal can elevate your footage to new heights, ensuring that every shot is as smooth and professional as possible.








































There are no comments for this blog.