How Do You Focus A Telescope?
Focusing a telescope is a fundamental skill for any amateur astronomer or stargazing enthusiast. Whether you are using a simple refractor telescope or a more complex reflector or compound telescope, achieving a sharp, clear image is essential for observing celestial objects in detail. In this article, we will explore the various steps and techniques involved in focusing a telescope, addressing common challenges and providing practical solutions to ensure you get the best possible view of the night sky.
Understanding the Basics of Telescope Focusing

Before diving into the specifics of focusing, it is important to understand the basic components of a telescope that are involved in this process. The primary components include:
1. Eyepiece: The lens or combination of lenses at the viewing end of the telescope.
2. Focuser: The mechanism that moves the eyepiece or the primary mirror to adjust the focus.
3. Objective Lens or Primary Mirror: The main optical element that gathers light.
The goal of focusing is to adjust the position of the eyepiece relative to the objective lens or primary mirror so that the light rays converge at the focal point, producing a sharp image.
Step-by-Step Guide to Focusing a Telescope
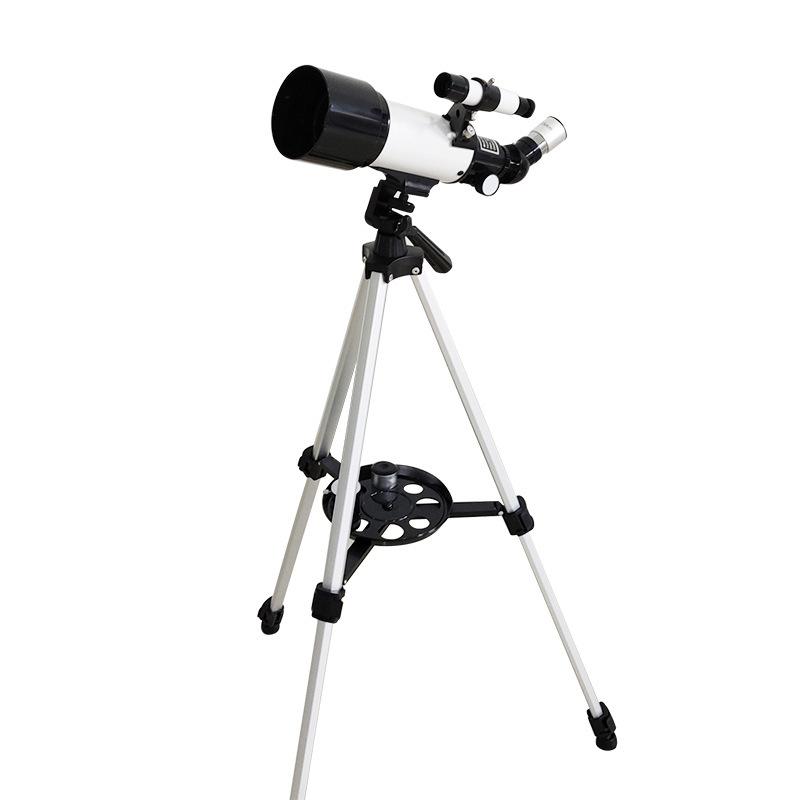

1. Initial Setup

- Stabilize the Telescope: Ensure that your telescope is securely mounted on a stable tripod or mount. Any movement or vibration can make focusing difficult.
- Align the Finderscope: Before focusing on your main target, align the finderscope with the main telescope. This will help you locate objects more easily.
2. Choosing the Right Eyepiece

- Start with a Low-Power Eyepiece: Begin with an eyepiece that has a longer focal length (lower magnification). This provides a wider field of view, making it easier to locate and center your target.
- Switch to Higher Power: Once you have centered your target, you can switch to a higher-power eyepiece for more detailed observation.
3. Focusing the Telescope
- Rough Focus: Use the focuser to make large adjustments. Turn the focuser knob slowly while looking through the eyepiece until the image starts to come into view.
- Fine Focus: Once the image is roughly in focus, make smaller adjustments to achieve a sharp image. Some telescopes have a dual-speed focuser, allowing for both coarse and fine adjustments.
4. Dealing with Common Issues
- Atmospheric Conditions: Turbulence in the Earth's atmosphere can cause the image to appear blurry. Wait for moments of steady air (known as "seeing") to fine-tune your focus.
- Temperature Differences: Allow your telescope to acclimate to the outdoor temperature. Rapid temperature changes can cause the optics to expand or contract, affecting focus.
- Collimation: For reflector telescopes, ensure that the mirrors are properly aligned. Misaligned mirrors can prevent you from achieving a sharp focus.
Advanced Focusing Techniques
1. Using a Focusing Mask
A focusing mask, such as a Bahtinov mask, can help achieve precise focus. This mask creates diffraction patterns that make it easier to determine the exact point of focus. Place the mask over the objective lens or aperture, and adjust the focus until the diffraction spikes converge.
2. Electronic Focusers
For those who want to take their focusing to the next level, electronic focusers can be a valuable tool. These devices allow for precise, motorized adjustments, often controlled via a computer or smartphone app. This can be particularly useful for astrophotography, where achieving perfect focus is critical.
Troubleshooting Focus Problems
1. Blurry Images
- Check Collimation: Ensure that the mirrors or lenses are properly aligned.
- Clean Optics: Dust or smudges on the lenses or mirrors can affect image quality. Use a soft brush or lens cleaning solution to clean the optics.
- Adjust Focus: Make sure you are using the correct eyepiece and that the focuser is functioning properly.
2. Double Images
- Check for Dew: Dew on the optics can cause double images. Use a dew shield or heater to prevent moisture buildup.
- Inspect the Eyepiece: Ensure that the eyepiece is properly seated and free of defects.
3. Difficulty Achieving Focus
- Use a Focusing Mask: A focusing mask can help achieve precise focus.
- Check for Mechanical Issues: Ensure that the focuser mechanism is smooth and free of obstructions.
Practical Tips for Better Focusing
- Practice in Daylight: Practice focusing on distant terrestrial objects during the day. This can help you become familiar with the focuser and eyepieces.
- Use a Red Flashlight: When adjusting focus at night, use a red flashlight to preserve your night vision.
- Take Your Time: Achieving perfect focus can take time and patience. Make small adjustments and observe the results.
Focusing a telescope is a skill that improves with practice and experience. By understanding the basic components and following a systematic approach, you can achieve sharp, clear images of celestial objects. Whether you are observing the moon, planets, or deep-sky objects, proper focus is essential for a rewarding stargazing experience. Remember to consider atmospheric conditions, temperature differences, and the alignment of your optics. With patience and attention to detail, you can master the art of focusing and enjoy the wonders of the night sky in all their glory.








































There are no comments for this blog.