How Does Wireless Cameras Get Power?
Wireless cameras have become an integral part of modern security systems, offering flexibility and ease of installation. However, one common question that arises is: how do these wireless cameras get power? Understanding the various power options available for wireless cameras can help you make an informed decision when setting up your security system. In this article, we will explore the different methods by which wireless cameras receive power, their advantages and disadvantages, and practical considerations for each option.
Battery-Powered Wireless Cameras

One of the most popular methods for powering wireless cameras is through batteries. Battery-powered wireless cameras are designed to be completely wire-free, making them incredibly easy to install and relocate as needed. These cameras typically use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, which can last anywhere from a few weeks to several months on a single charge, depending on usage and camera settings.
Advantages:

1. Ease of Installation: Since there are no wires to run, battery-powered cameras can be installed virtually anywhere.
2. Flexibility: These cameras can be easily moved to different locations as needed.
3. No Power Outage Concerns: Battery-powered cameras continue to operate during power outages, ensuring continuous surveillance.
Disadvantages:

1. Battery Life: The need to recharge or replace batteries can be inconvenient, especially in high-traffic areas where the camera is frequently triggered.
2. Performance: Some battery-powered cameras may have limited features to conserve battery life, such as reduced video quality or shorter recording times.
Solar-Powered Wireless Cameras
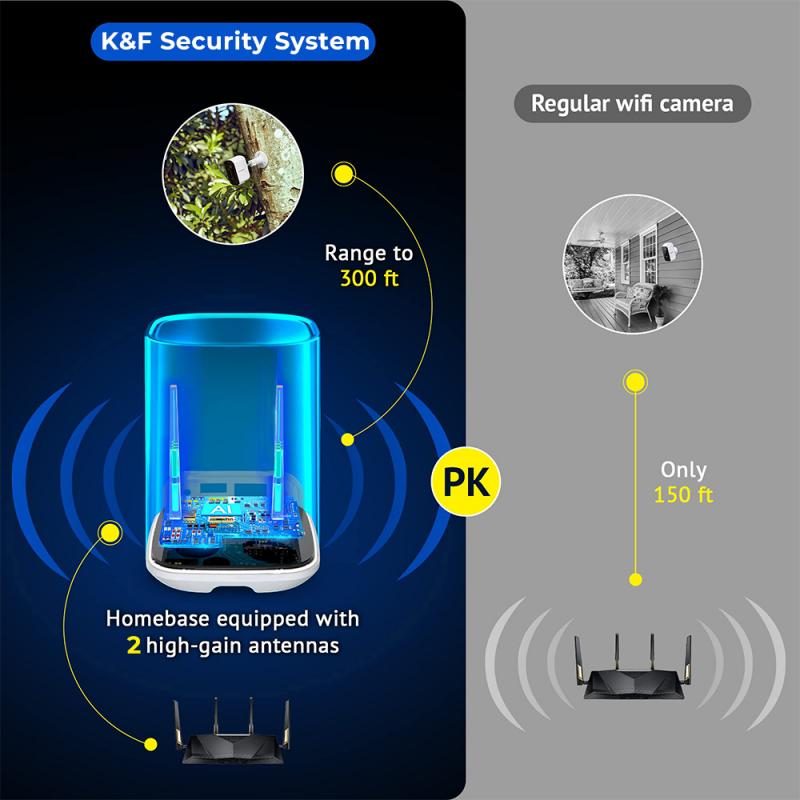
Solar-powered wireless cameras are an eco-friendly option that combines the benefits of battery power with the sustainability of solar energy. These cameras are equipped with solar panels that continuously recharge the internal batteries, reducing the need for manual recharging.
Advantages:
1. Sustainability: Solar power is a renewable energy source, making these cameras environmentally friendly.
2. Low Maintenance: With continuous solar charging, the need for manual battery replacement or recharging is significantly reduced.
3. Remote Locations: Ideal for remote or off-grid locations where traditional power sources are unavailable.
Disadvantages:
1. Weather Dependency: Solar-powered cameras rely on sunlight, so their performance can be affected by weather conditions and the amount of sunlight available.
2. Initial Cost: The initial investment for solar-powered cameras and panels can be higher compared to other options.
Plug-In Wireless Cameras
Plug-in wireless cameras are powered by connecting them to an electrical outlet using a power adapter. While these cameras are still considered wireless in terms of data transmission, they do require a constant power source.
Advantages:
1. Continuous Power: Plug-in cameras provide uninterrupted power, ensuring consistent performance and recording.
2. Advanced Features: These cameras often come with advanced features such as higher resolution, continuous recording, and enhanced night vision, as they are not limited by battery life.
Disadvantages:
1. Installation Constraints: The need for a nearby power outlet can limit installation options and may require additional wiring.
2. Power Outages: These cameras are susceptible to power outages unless paired with a backup power source like an uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Wireless Cameras
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology allows cameras to receive both power and data through a single Ethernet cable. While PoE cameras are typically associated with wired systems, there are hybrid models that offer wireless data transmission while still using PoE for power.
Advantages:
1. Single Cable Solution: PoE simplifies installation by combining power and data transmission into one cable.
2. Reliable Power: Provides a stable and continuous power source, ensuring consistent camera performance.
3. Scalability: PoE systems are easily scalable, making them suitable for larger installations.
Disadvantages:
1. Wiring Requirements: Despite being wireless in data transmission, PoE cameras still require Ethernet cabling for power, which can complicate installation.
2. Cost: PoE switches and injectors can add to the overall cost of the system.
Hybrid Power Solutions
Some wireless cameras offer hybrid power solutions, combining multiple power sources to enhance reliability and flexibility. For example, a camera may use a combination of solar power and battery backup, or PoE with a battery backup.
Advantages:
1. Enhanced Reliability: Combining power sources ensures continuous operation even if one source fails.
2. Flexibility: Hybrid solutions can be tailored to specific needs and environments.
Disadvantages:
1. Complexity: Managing multiple power sources can add complexity to the installation and maintenance process.
2. Cost: Hybrid systems can be more expensive due to the need for additional components.
Practical Considerations
When choosing a power solution for your wireless cameras, consider the following practical factors:
1. Location: Assess the installation site to determine the most suitable power option. For example, remote locations may benefit from solar power, while urban settings with accessible power outlets may be better suited for plug-in cameras.
2. Usage: Consider how frequently the camera will be used and the features required. High-traffic areas may drain batteries quickly, making plug-in or PoE options more practical.
3. Budget: Evaluate the initial and ongoing costs associated with each power option. While battery-powered cameras may have lower upfront costs, the need for frequent battery replacements can add up over time.
4. Environmental Factors: Take into account weather conditions and other environmental factors that may impact the performance of solar-powered or battery-powered cameras.
Wireless cameras offer a range of power options to suit different needs and environments. Whether you opt for battery-powered, solar-powered, plug-in, PoE, or hybrid solutions, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method will help you make an informed decision. By considering factors such as location, usage, budget, and environmental conditions, you can select the most appropriate power solution for your wireless camera system, ensuring reliable and continuous surveillance for your property.









































There are no comments for this blog.