How To Store Camera Batteries?
Properly storing camera batteries is crucial for maintaining their longevity and ensuring they are ready for use when needed. Whether you are a professional photographer or an amateur enthusiast, understanding the best practices for battery storage can save you time, money, and frustration. In this article, we will explore various aspects of storing camera batteries, including the types of batteries, storage conditions, and maintenance tips to keep them in optimal condition.
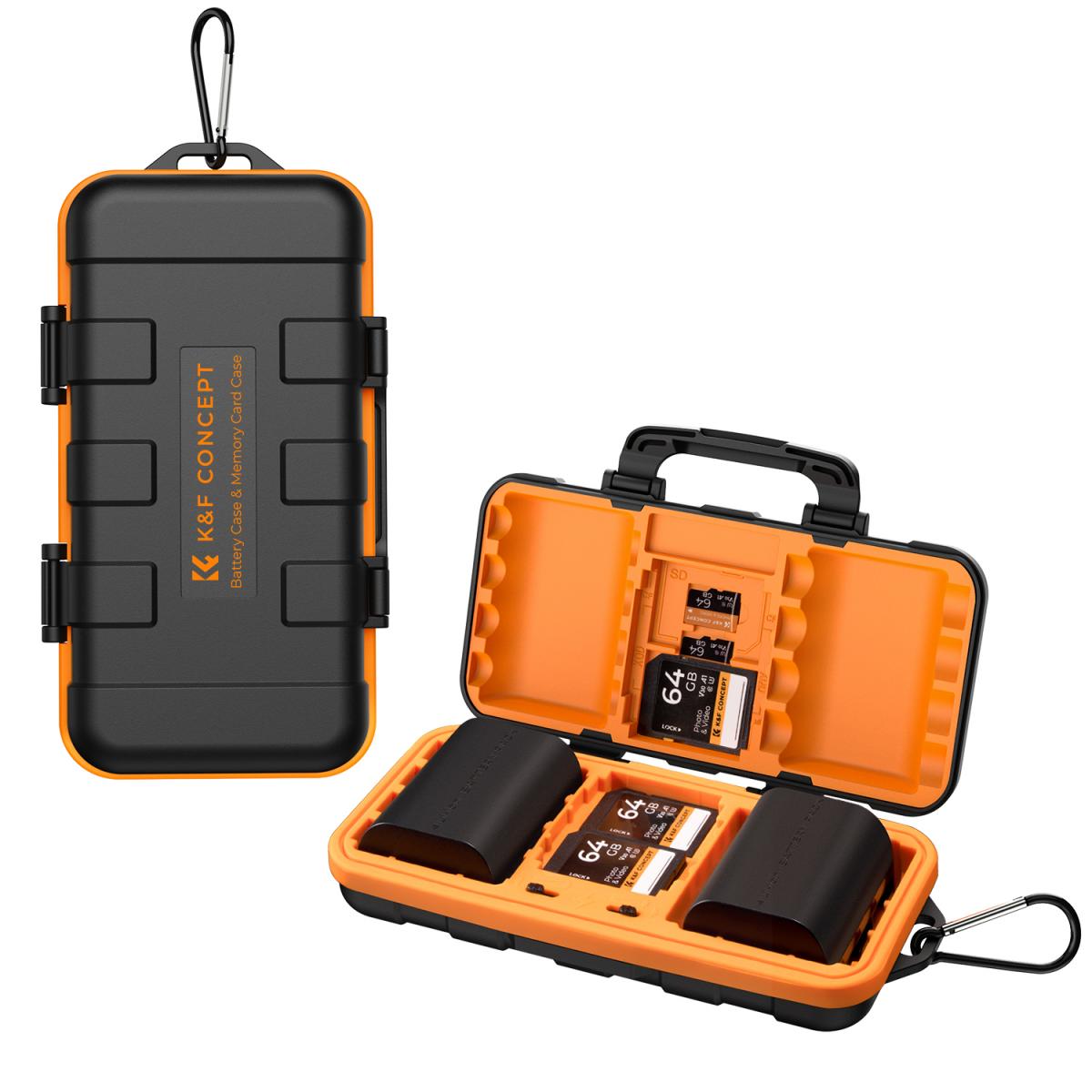

Understanding Camera Battery Types
Before diving into storage techniques, it is essential to understand the different types of camera batteries. The most common types are:
1. Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: These are the most popular due to their high energy density, lightweight, and long lifespan. They are commonly used in DSLRs, mirrorless cameras, and other high-end devices.
2. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: These are often used in older camera models and some point-and-shoot cameras. They are rechargeable but have a lower energy density compared to Li-Ion batteries.
3. Alkaline Batteries: These are non-rechargeable and typically used in low-end or disposable cameras. They are not ideal for long-term use due to their limited lifespan and lower energy output.
Ideal Storage Conditions
The environment in which you store your camera batteries plays a significant role in their longevity and performance. Here are some key factors to consider:
Temperature
- Optimal Temperature Range: Store batteries in a cool, dry place with a temperature range between 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Extreme temperatures can degrade battery performance and lifespan.
- Avoid Freezing Temperatures: Storing batteries in freezing conditions can cause irreversible damage. If you must store them in a cold environment, ensure they are insulated and gradually bring them to room temperature before use.
- High Temperatures: Avoid storing batteries in hot environments, such as a car on a sunny day, as this can lead to overheating and potential leakage or explosion.
Humidity

- Low Humidity: High humidity can cause corrosion and damage to the battery contacts. Store batteries in a dry environment with low humidity levels.
- Use Silica Gel Packs: To control humidity, consider using silica gel packs in your storage container. These packs absorb moisture and help maintain a dry environment.
Storage Techniques
Proper storage techniques can significantly impact the lifespan and performance of your camera batteries. Here are some best practices:
Partial Charge
- Li-Ion Batteries: Store Li-Ion batteries at around 40-60% charge. Storing them fully charged or completely drained can reduce their lifespan.
- NiMH Batteries: These can be stored either fully charged or partially charged, but it is generally recommended to store them with a partial charge to avoid self-discharge.
Separate Storage
- Remove from Camera: Always remove batteries from the camera when not in use for extended periods. This prevents potential leakage and damage to the camera.
- Individual Storage: Store batteries individually in protective cases or plastic bags to prevent short-circuiting. Ensure the battery terminals are covered to avoid contact with metal objects.
Regular Maintenance
- Periodic Charging: For long-term storage, periodically check and recharge your batteries every 3-6 months. This helps maintain their capacity and prevents deep discharge.
- Cleaning Contacts: Clean the battery contacts with a dry cloth or an alcohol wipe before storage. This ensures good electrical contact and prevents corrosion.
Special Considerations
Different scenarios may require specific storage considerations. Here are some additional tips:
Traveling
- Carry-On Luggage: When traveling by air, always carry camera batteries in your carry-on luggage. Airlines have strict regulations regarding the transport of lithium batteries in checked baggage due to fire risks.
- Battery Cases: Use protective battery cases to prevent short-circuiting and physical damage during travel.
Long-Term Storage
- Dedicated Storage Area: If you need to store batteries for an extended period, designate a specific area for battery storage. This area should be cool, dry, and away from direct sunlight.
- Labeling: Label your batteries with the date of purchase and the last charge date. This helps you keep track of their age and maintenance schedule.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with proper storage, you may encounter some common battery issues. Here are solutions to a few problems:
Reduced Capacity
- Reconditioning: For NiMH batteries, you can try reconditioning by fully discharging and then fully charging them a few times. This can help restore some lost capacity.
- Replacement: If a battery consistently shows reduced capacity despite proper storage and maintenance, it may be time to replace it.
Swelling or Leakage
- Immediate Disposal: If you notice any swelling, leakage, or unusual odor from a battery, dispose of it immediately. Do not attempt to use or recharge it.
- Safe Disposal: Follow local regulations for the safe disposal of batteries. Many communities have designated recycling centers for electronic waste.
Proper storage of camera batteries is essential for maintaining their performance and extending their lifespan. By understanding the types of batteries, ideal storage conditions, and best practices for maintenance, you can ensure that your batteries are always ready for use. Whether you are storing them for a short period or long-term, following these guidelines will help you avoid common issues and keep your photography gear in top condition. Remember, a well-maintained battery not only saves you money but also ensures that you never miss capturing those perfect moments.










































There are no comments for this blog.