How To Use Polarized Lens Filter?
Polarized lens filters are essential tools for photographers and videographers who want to enhance the quality of their images by reducing glare and reflections. These filters can make a significant difference in the clarity and color saturation of your photos, especially when shooting in bright sunlight or near reflective surfaces like water or glass. In this article, we will delve into the practical aspects of using polarized lens filters, covering everything from the basics to advanced techniques. By the end, you should have a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively use these filters to improve your photography.
Understanding Polarized Lens Filters

Before diving into the practical usage, it's crucial to understand what polarized lens filters are and how they work. A polarized lens filter is a piece of optical glass that is mounted in front of your camera lens. It works by filtering out polarized light, which is light that has been reflected off surfaces like water, glass, or even the atmosphere. This type of light often causes glare and reduces the overall quality of your images.
Types of Polarized Filters

There are two main types of polarized filters: linear and circular.
1. Linear Polarizers: These are the original type of polarizing filters and are still used in some applications. However, they can interfere with the autofocus and metering systems of modern digital cameras.
2. Circular Polarizers (CPL): These are more commonly used today because they are compatible with modern camera systems. They consist of a linear polarizer followed by a quarter-wave plate, which converts the linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light, allowing the camera's autofocus and metering systems to function correctly.
When to Use a Polarized Lens Filter
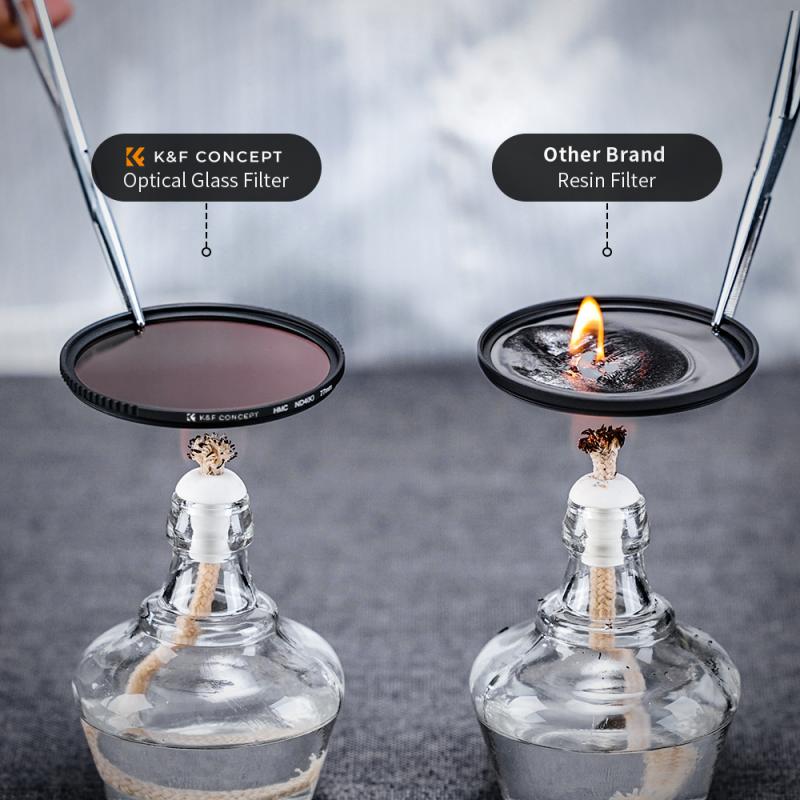

Polarized lens filters are particularly useful in the following scenarios:
1. Reducing Glare and Reflections: When shooting scenes with water, glass, or other reflective surfaces, a polarized filter can significantly reduce glare and reflections, allowing you to capture more detail.
2. Enhancing Colors: Polarized filters can make colors appear more vibrant and saturated, especially in outdoor settings. They are particularly effective for enhancing the blue of the sky and the green of foliage.
3. Improving Contrast: By reducing the amount of scattered light, polarized filters can improve the overall contrast of your images, making them appear sharper and more defined.
How to Use a Polarized Lens Filter

Using a polarized lens filter is relatively straightforward, but there are some key steps and tips to keep in mind:
1. Attach the Filter: Screw the polarized filter onto the front of your camera lens. Make sure it is securely attached but not overly tight, as this can make it difficult to remove later.
2. Adjust the Filter: Most polarized filters are adjustable. Once the filter is attached, you can rotate it to achieve the desired effect. Look through the viewfinder or at the live view screen while rotating the filter to see how it affects the image. The effect will be most noticeable when the filter is at a 90-degree angle to the light source.
3. Check the Exposure: Polarized filters can reduce the amount of light entering the lens by 1-2 stops. This means you may need to adjust your exposure settings to compensate. Use your camera's exposure meter to ensure you are getting the correct exposure.
4. Avoid Over-Polarization: In some cases, using a polarized filter can result in an unnatural look, especially if the sky becomes too dark or the colors too saturated. Be mindful of this and adjust the filter accordingly to achieve a natural-looking image.
Advanced Techniques
Once you are comfortable with the basics, you can experiment with more advanced techniques to get the most out of your polarized lens filter:
1. Combining Filters: You can use a polarized filter in combination with other types of filters, such as neutral density (ND) filters, to achieve specific effects. For example, combining a CPL with an ND filter can allow you to use slower shutter speeds in bright conditions, creating motion blur in water or clouds.
2. Using Polarized Filters in Portrait Photography: While polarized filters are most commonly used in landscape photography, they can also be useful in portrait photography. They can help reduce reflections on glasses or shiny skin, resulting in more flattering portraits.
3. Polarized Filters in Video: If you are shooting video, a polarized filter can help reduce glare and reflections, resulting in cleaner, more professional-looking footage. Just be mindful of the potential for over-polarization, as mentioned earlier.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced photographers can make mistakes when using polarized filters. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
1. Vignetting: Using a polarized filter on a wide-angle lens can sometimes cause vignetting, where the corners of the image appear darker. To avoid this, use a slim-profile filter designed for wide-angle lenses.
2. Uneven Polarization: When using a polarized filter on a wide-angle lens, you may notice uneven polarization, where the effect is stronger in some parts of the image than others. This is due to the angle of the light and is more noticeable in the sky. To minimize this, avoid using polarized filters on ultra-wide-angle lenses.
3. Forgetting to Adjust the Filter: It's easy to forget to adjust the filter after attaching it to your lens. Always remember to rotate the filter to achieve the desired effect before taking your shot.
Polarized lens filters are powerful tools that can significantly enhance the quality of your photographs by reducing glare, improving color saturation, and increasing contrast. By understanding how these filters work and following the tips and techniques outlined in this article, you can make the most of your polarized lens filter and take your photography to the next level. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced photographer, mastering the use of polarized filters can open up new creative possibilities and help you capture stunning images in a variety of conditions.































There are no comments for this blog.