What Filter To Use On Camera?
When it comes to photography, one of the most common questions that both amateur and professional photographers ask is, "What filter should I use on my camera?" This question is crucial because the right filter can significantly enhance the quality of your photos, adding depth, contrast, and vibrancy that might otherwise be missing. In this article, we will delve into the various types of camera filters available, their specific uses, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Understanding Camera Filters

Camera filters are accessories that photographers attach to the front of their camera lenses. They serve various purposes, from protecting the lens to enhancing the image quality. Filters can be made from glass, resin, or polyester, and they come in different shapes and sizes to fit various lenses.
Types of Camera Filters

1. UV Filters
- Purpose: UV filters are primarily used to block ultraviolet light, which can cause haziness and reduce the clarity of your photos. They also serve as a protective layer for your lens.
- When to Use: These filters are particularly useful in high-altitude or coastal areas where UV light is more intense. They are also a good everyday filter to protect your lens from dust, scratches, and smudges.
2. Polarizing Filters
- Purpose: Polarizing filters reduce reflections and glare from non-metallic surfaces like water and glass. They also enhance the colors and contrast in your photos.
- When to Use: Use polarizing filters when shooting landscapes, especially when you want to capture vibrant skies and reduce reflections from water bodies. They are also useful for shooting through glass windows.
3. Neutral Density (ND) Filters
- Purpose: ND filters reduce the amount of light entering the lens without affecting the color of the image. This allows for longer exposure times and wider apertures.
- When to Use: These filters are ideal for landscape photography, especially when you want to capture motion blur in waterfalls, rivers, or clouds. They are also useful for shooting in bright conditions where you want to use a wide aperture for a shallow depth of field.
4. Graduated Neutral Density (GND) Filters
- Purpose: GND filters are similar to ND filters but have a gradient that transitions from dark to clear. This helps balance the exposure between the sky and the ground.
- When to Use: These filters are perfect for landscape photography, particularly during sunrise or sunset when the sky is much brighter than the foreground.
5. Color Filters
- Purpose: Color filters alter the color balance of your photos. They can be used to enhance certain colors or create special effects.
- When to Use: These filters are often used in black and white photography to increase contrast. For example, a red filter can make the sky appear darker, adding drama to the image.
6. Infrared (IR) Filters
- Purpose: IR filters block visible light and allow only infrared light to pass through, creating surreal and otherworldly images.
- When to Use: Use these filters for creative and experimental photography. They are particularly effective in landscape photography, where they can make foliage appear white and skies dark.
How to Choose the Right Filter

Choosing the right filter depends on several factors, including the type of photography you are interested in, the lighting conditions, and the specific effects you want to achieve. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
1. Identify Your Needs: Determine what you want to achieve with the filter. Are you looking to protect your lens, reduce reflections, balance exposure, or create special effects?
2. Consider the Lighting Conditions: Different filters are suited for different lighting conditions. For example, ND filters are great for bright conditions, while polarizing filters are ideal for reducing glare in sunny environments.
3. Check Compatibility: Ensure that the filter you choose is compatible with your lens. Filters come in various sizes, so you need to know the diameter of your lens to get the right fit.
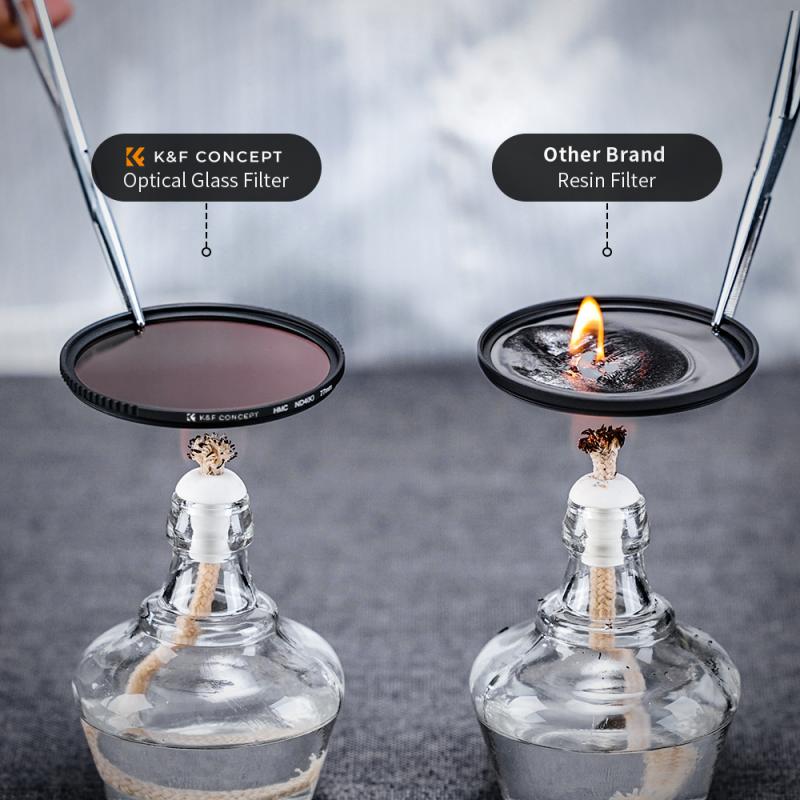
4. Quality Matters: Invest in high-quality filters. Cheap filters can degrade the image quality, introducing unwanted artifacts and reducing sharpness.
5. Experiment: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different filters to see what works best for you. Photography is an art, and sometimes the best way to learn is through trial and error.
Practical Applications

To give you a better understanding of how these filters can be used in real-world scenarios, let’s look at some practical applications:
1. Landscape Photography: For landscape photography, a combination of polarizing and ND filters can work wonders. The polarizing filter will enhance the colors and reduce reflections, while the ND filter will allow you to use longer exposure times to capture motion blur in water or clouds.
2. Portrait Photography: In portrait photography, UV filters can protect your lens, while ND filters can help you achieve a shallow depth of field even in bright conditions. This can make your subject stand out against a beautifully blurred background.
3. Architectural Photography: When shooting buildings, polarizing filters can help reduce reflections from windows and enhance the colors of the structure. GND filters can also be useful if you are shooting at times when the sky is much brighter than the building.
4. Creative Photography: For those looking to experiment, color and IR filters can open up a world of creative possibilities. Use color filters to add mood and drama to your black and white photos, or IR filters to create surreal landscapes that look like they are from another planet.
Camera filters are essential tools that can significantly enhance your photography. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned professional, understanding the different types of filters and their uses can help you take your photos to the next level. By carefully selecting the right filter for your needs and experimenting with different options, you can achieve stunning results that capture the beauty and essence of your subjects. So, the next time you ask yourself, "What filter should I use on my camera?" you’ll have a clear and informed answer.