How Smart Lock Works?
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, the evolution of traditional devices has drastically reshaped daily life. Among such advancements is the smart lock—a modern alternative to conventional locks that integrates technology for enhanced convenience, security, and functionality. Smart locks have gained significant traction in both residential and commercial markets, owing to their practicality and ability to seamlessly integrate with smart home ecosystems. This article delves into the mechanics of smart locks, offering insights into how they function, the technologies involved, and the benefits they offer.
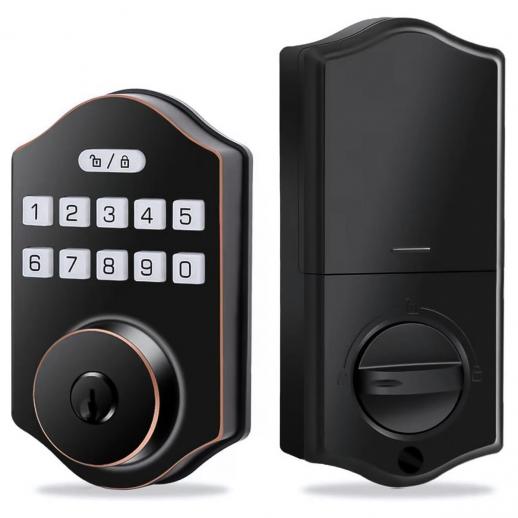

What Is a Smart Lock?
A smart lock is an electronic and often wireless-enabled locking mechanism designed to replace or supplement traditional mechanical locks. Unlike standard locks that rely solely on physical keys, smart locks leverage digital inputs such as passcodes, biometrics, or smartphone commands to control access. These devices can connect to home automation systems or mobile applications, allowing users to lock, unlock, or monitor their doors remotely.
---
Key Components of Smart Locks
To understand how smart locks work, it’s essential to identify their core components, each contributing to their functionality:
1. Lock Mechanism:
- The actual locking hardware, which can be a deadbolt or latch mechanism, remains similar to traditional locks but is electronically controlled.
2. Digital Authentication Module:
- This module processes input data, such as passcodes, fingerprints, or encrypted signals from a smartphone or key fob, to verify user credentials.
3. Connectivity Interface:
- Smart locks rely on wireless communication protocols, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or Zigbee, to interface with other devices or systems.
4. Power Source:
- Most smart locks are battery-powered, ensuring operation even during power outages. They typically alert users when battery levels are low.
5. Mobile App or Control Panel:
- An app or integrated system allows users to manage access, set permissions, and receive alerts.
6. Sensors:
- Smart locks may include sensors to detect door alignment, tampering attempts, or unauthorized access.
---
How Smart Locks Work
Smart locks function by combining mechanical locking mechanisms with electronic and digital technologies. Below is a detailed step-by-step process of their operation:
1. Authentication:
- The user initiates an unlocking command via one of several methods:
- Passcode Entry: The user inputs a numerical code into a keypad or touchscreen.
- Biometric Verification: A fingerprint or facial recognition scan is performed.
- Digital Key: A smartphone sends an encrypted unlocking signal via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Voice Command: Compatible smart locks can respond to voice assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant.
2. Verification:
- The lock’s processor verifies the credentials using its embedded algorithms. For instance:
- Passcodes are matched against stored data.
- Biometric data is compared to pre-registered templates.
- Encrypted signals are decoded to ensure authenticity.
3. Actuation:
- Upon successful authentication, the electronic actuator engages to retract the bolt or latch, unlocking the door. Similarly, the same process works in reverse for locking.
4. Feedback and Monitoring:
- Smart locks provide immediate feedback through audio cues, LED indicators, or notifications via mobile apps, confirming whether the door is locked or unlocked.
- Advanced models also log access events, enabling users to track who entered and when.
5. Remote Access:
- Wi-Fi-enabled smart locks allow users to operate them remotely, monitor access logs, or grant temporary permissions. This is particularly useful for property managers or homeowners who frequently host guests.
---
Advantages of Smart Locks
The growing popularity of smart locks is attributed to the numerous benefits they offer, such as:
1. Enhanced Security:
- Smart locks eliminate vulnerabilities associated with physical keys, such as duplication or loss. Features like automatic locking and real-time alerts further bolster security.
2. Convenience:
- Forgetting or misplacing keys is no longer a concern. Users can lock or unlock doors with their smartphones or even grant access to others remotely.
3. Integration with Smart Ecosystems:
- Smart locks integrate seamlessly with home automation systems, enabling actions such as locking doors when a security system is armed or turning off lights when leaving the house.
4. Customizable Access:
- Temporary or restricted access can be granted to specific individuals, such as house cleaners, delivery personnel, or guests, without sharing physical keys.
5. Monitoring and Insights:
- Many smart locks provide detailed logs of access events, enhancing transparency and control.
6. Energy Efficiency:
- Smart locks are designed to be energy-efficient, operating on minimal power and ensuring extended battery life.
---
Challenges and Considerations
While smart locks offer numerous advantages, they are not without challenges:
1. Battery Dependence:
- A dead battery can render a smart lock inoperable. Manufacturers mitigate this risk by including backup options, such as physical keys or emergency power terminals.
2. Cybersecurity Risks:
- As connected devices, smart locks are vulnerable to hacking. Users must ensure robust security practices, such as using strong passwords and updating firmware regularly.
3. Cost:
- Smart locks are generally more expensive than traditional locks, though the added functionality often justifies the investment.
4. Compatibility Issues:
- Some smart locks may not fit all doors or align seamlessly with certain home automation systems.
5. Connectivity Limitations:
- Poor Wi-Fi or Bluetooth signals can impact performance, especially for remote access features.
---
Popular Technologies in Smart Locks
Smart locks utilize various technologies to deliver their functionality:
1. Bluetooth:
- Ideal for proximity-based access. The lock connects to a user’s smartphone when within range, enabling unlocking without internet connectivity.
2. Wi-Fi:
- Offers remote access and real-time notifications. However, Wi-Fi drains batteries faster than other protocols.
3. Zigbee/Z-Wave:
- These low-power protocols are common in home automation systems. They require a hub but consume less power than Wi-Fi.
4. NFC and RFID:
- These technologies allow users to unlock doors using cards or compatible devices.
5. Biometric Sensors:
- Advanced locks include fingerprint or facial recognition capabilities for added security.
---
Future Trends in Smart Locks
The smart lock market continues to evolve, driven by innovations and consumer demand. Key trends include:
1. AI Integration:
- Artificial intelligence will enhance predictive features, such as automatically locking doors when users leave or adjusting permissions based on usage patterns.
2. Blockchain for Security:
- Blockchain technology could be employed to secure authentication processes and enhance trustworthiness.
3. Energy Harvesting:
- Future smart locks may feature energy-harvesting mechanisms to reduce dependency on batteries.
4. Universal Compatibility:
- Manufacturers are moving towards standardizing protocols to improve compatibility with various systems and devices.
5. Voice and Gesture Recognition:
- More intuitive interfaces will allow users to interact with smart locks through voice commands or gestures.
---
Practical Applications of Smart Locks
1. Residential Use:
- Homeowners use smart locks for convenience, security, and integration with smart home ecosystems.
2. Commercial Properties:
- Offices and co-working spaces utilize smart locks for access management and security.
3. Hospitality Sector:
- Hotels and vacation rentals employ smart locks for seamless guest check-ins and check-outs.
4. Healthcare Facilities:
- Hospitals and clinics use smart locks to restrict access to sensitive areas.
---
Smart locks represent a significant leap forward in security technology, offering a blend of convenience, flexibility, and enhanced protection. Understanding their mechanics and potential applications can help users make informed decisions when integrating these devices into their homes or businesses. As technology advances, smart locks are poised to become an integral part of modern living, reflecting the future of secure and connected environments. Whether you are a homeowner seeking convenience or a business owner looking to optimize access management, the adoption of smart locks offers a pathway to smarter, safer living.




































There are no comments for this blog.