What Are Microscope Slides Used For?
Microscopes have revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world, allowing scientists, researchers, students, and medical professionals to observe and study specimens in remarkable detail. One of the most essential components of using a microscope effectively is the microscope slide. These small, flat pieces of glass or plastic are integral to the preparation, observation, and analysis of various samples. In this article, we will delve into the numerous uses of microscope slides, covering their types, preparation methods, and applications across different fields. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the significance of microscope slides and how they contribute to advancements in science and medicine.
Microscopy: A World Beyond the Naked Eye

Microscopy encompasses techniques and tools that allow the observation of objects and details that cannot be seen with the unaided human eye. Microscope slides play a crucial role in this field by providing a stable and clear platform for viewing specimens. The basic principles of microscopy require a sample to be thin enough for light or electrons to pass through, and microscope slides fulfill this requirement efficiently.
Types of Microscope Slides
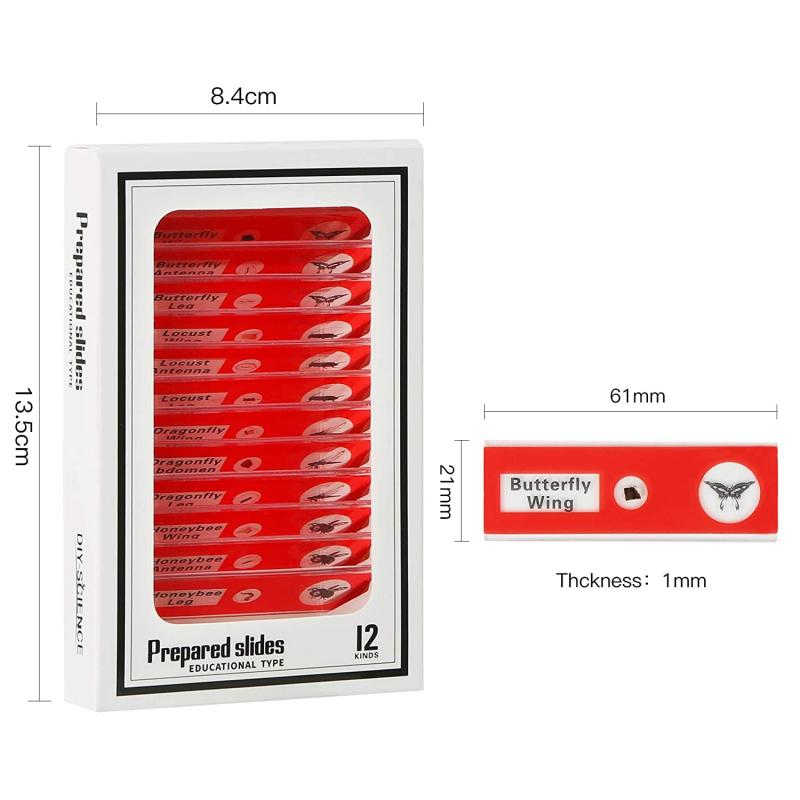

Several types of microscope slides are used depending on the needs of the observation:
1. Standard Glass Slides: These are the most common type, used for a wide variety of specimens. They are typically 1 mm thick and measure about 25 x 75 mm.
2. Frosted Slides: These slides have an area that is roughened or frosted, allowing for easy labeling with pencils or markers. This is particularly useful in clinical and research settings where accurate identification is crucial.
3. Concave Slides: Featuring a small depression or well, concave slides are used for studying liquid samples, living organisms, or larger particulate matter that might move out of the focus plane on a flat slide.
4. Adhesive Slides: These slides have a sticky surface to help hold samples in place. They are used for delicate specimens that might otherwise shift or become damaged during examination.
Preparation of Microscope Slides

The process of preparing microscope slides is essential for accurate and meaningful observations. Preparation methods vary based on the type of sample being studied and the kind of analysis required. Here are common preparation techniques:
1. Dry Mounting: This involves placing a dry specimen directly onto the slide. A cover slip is often used to protect the sample and enable clear visualization. This method is suitable for hair, pollen, dust particles, and other solid samples.
2. Wet Mounting: In wet mounting, a liquid (usually water or a stain) is added to the specimen on the slide. A cover slip is added to reduce evaporation and to flatten the sample. This technique is common for observing living microorganisms or cells in fluids.
3. Staining: Certain biological specimens are transparent and need to be stained to enhance contrast. Dyes or stains bind to specific components of the sample, making structures like cell walls, nuclei, and organelles more visible.
4. Smear: A smear involves spreading a thin layer of the sample across the slide. This is commonly used for blood samples or bacterial cultures, where individual cells can be better observed when spread out.
5. Sectioning: Thinly slicing specimens using a microtome or razor blade is necessary for thicker samples like tissues. These sections are then placed on the slide for examination.
Applications Across Various Fields

Microscope slides have vast applications across numerous fields of science and medicine. Their role is indispensable in the following areas:
1. Biology and Research: Microscope slides are fundamental in biological research for studying cell structure, function, and interactions. They allow scientists to observe cellular processes, identify microorganisms, and conduct genetic research.
2. Medical Diagnostics: In clinical settings, slides are used to examine blood, tissue, and other body fluids. Pathologists use slides to detect and diagnose diseases, such as cancer through biopsy samples, and to identify pathogens in infectious diseases.
3. Education: Students in biology, botany, zoology, and microbiology courses use microscope slides to learn about the microscopic world. Prepared slides of various specimens help enhance their understanding of complex biological concepts.
4. Environmental Science: Researchers use microscope slides to study samples from water bodies, soil, and air to monitor environmental health. Observing particulate matter, plankton, and microorganisms assists in assessing pollution levels and ecosystem conditions.
5. Forensic Science: Forensic experts use microscope slides for analyzing evidence such as fibers, hair, and bodily fluids from crime scenes. Microscopic analysis of such evidence can provide crucial information for criminal investigations.
Advancements in Microscope Slide Technology
With advancements in technology, microscope slides are not just simple glass pieces anymore. Modern innovations have led to the development of specialized slides that enhance the efficiency and accuracy of observations.
1. Coated Slides: These slides have coatings that promote adhesion of specific cell types or tissues, improving sample quality and stability.
2. Fluorescent Slides: Such slides are used in fluorescence microscopy, where they are designed to minimize autofluorescence and background noise.
3. Automated Slide Preparation: Automated systems for slide preparation are becoming more common in clinical labs. They ensure the consistency and quality of slides, especially important in high-throughput environments.
4. Digital Slides: With advancements in digital microscopy, traditional slides can be scanned and converted into digital images. Digital slides can be easily shared online, facilitating remote analysis and collaborative research.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their utility, the use of microscope slides comes with certain challenges and important considerations:
1. Sample Integrity: The process of preparing a slide can sometimes alter the sample. Ensuring the integrity of the specimen is crucial for accurate analysis.
2. Staining Artifacts: Improper staining techniques can introduce artifacts that might be mistaken for actual sample features. Careful technique and experience are required to differentiate artifacts from real structures.
3. Handling and Storage: Slides are delicate and must be handled with care to prevent breakage and contamination. Proper storage conditions are essential to maintain sample integrity over time.
Microscope slides are indispensable tools in the observation and study of the microscopic world. From biological research to medical diagnostics and environmental studies, their applications are vast and varied. Advances in technology continue to enhance the functionality and efficiency of microscope slides, making them more than just simple pieces of glass or plastic.
Understanding the different types, preparation methods, and applications of microscope slides equips professionals and students with the knowledge to utilize this tool effectively. As microscopy continues to evolve, the humble microscope slide remains a cornerstone, enabling discoveries and insights that transform our understanding of the natural and scientific world.






































There are no comments for this blog.