What Is Axis Lighting In Photography?
In the vast realm of photography, light is not just a mere necessity; it is a tool that can completely alter the character and feel of an image. Among the various techniques used by photographers to manipulate and manage light, axis lighting stands out as a sophisticated yet accessible method to achieve compelling results. This approach to lighting not only enhances the aesthetics of a photograph but also provides photographers with the ability to precisely control mood, depth, and texture. In this article, we delve deep into the concept of axis lighting, exploring its nuances, applications, and practical tips to master the technique.
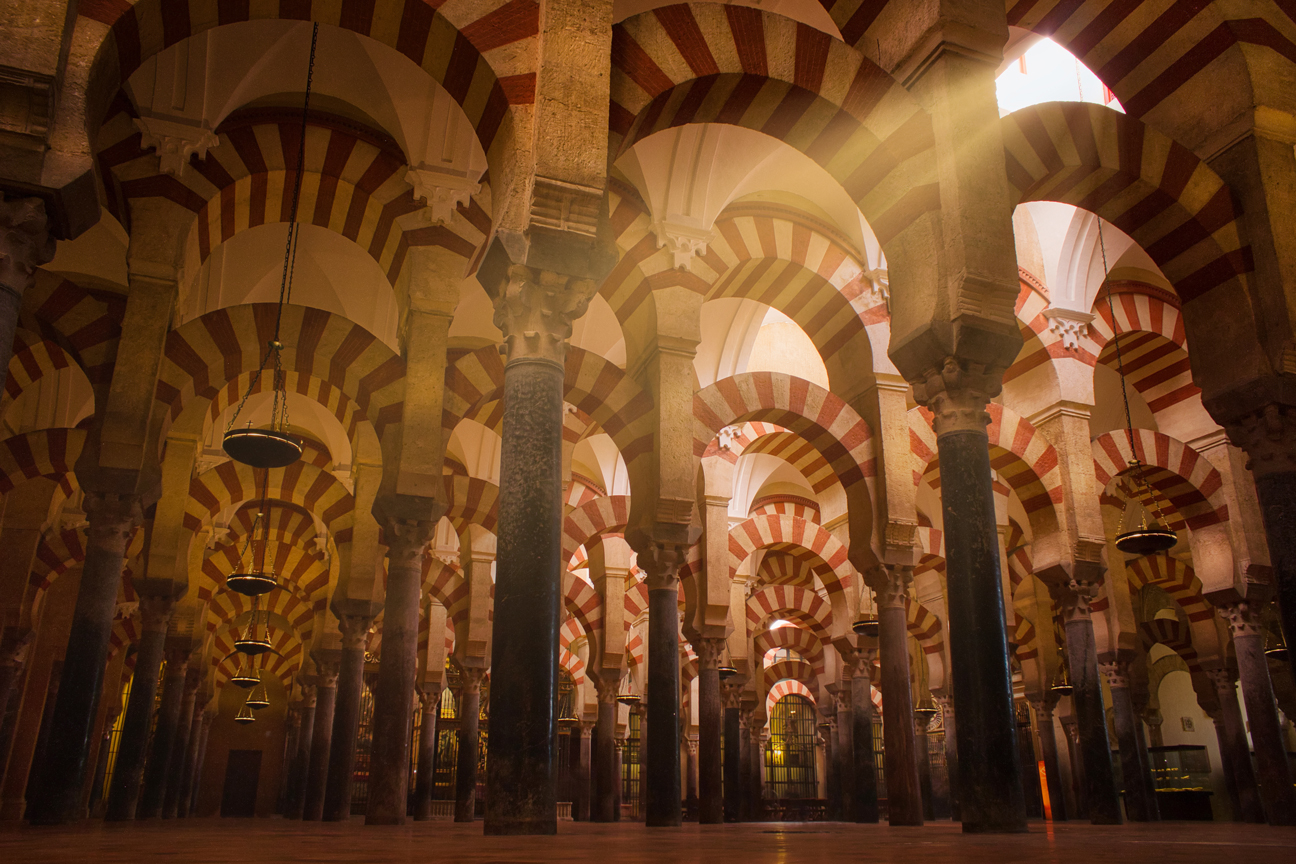

Understanding Axis Lighting
Axis lighting, also known as on-axis lighting, refers to the illumination that originates from a light source aligned along the same axis as the camera lens. In other words, the light source is directly behind the camera, essentially pointing in the same direction as the photographer's field of view. This setup ensures that the light strikes the subject head-on, minimizing shadows and evenly distributing light across the surface.
The primary characteristic of axis lighting is its ability to create flat, shadow-free images. This trait can be particularly useful in various photographic scenarios but also poses the challenge of possibly rendering an image too flat or lacking in depth if not used judiciously.
Applications of Axis Lighting in Photography
1. Portraiture:
One of the most common uses of axis lighting is in portrait photography. By lighting the subject directly from in front of the camera, the technique helps in eliminating harsh shadows that might obscure facial features. This can be especially beneficial for high-key portraits, beauty shots, and fashion photography, where even, soft lighting accentuates skin tones and textures.
2. Product Photography:
When photographing products, especially for commercial purposes, axis lighting can ensure that all details are clearly visible without distracting shadows. It helps in presenting the product in a clear and appealing manner. This is crucial in e-commerce where product images need to convey as much information as possible to potential buyers.
3. Documentary and Forensic Photography:
Axis lighting is utilized in fields like documentary and forensic photography to achieve clear, detailed images. The shadowless illumination is ideal for capturing fine details in objects, artworks, or scenes that require precise documentation without the interference of shadows that might obscure specific parts.
4. Macro Photography:
In macro photography, where subjects are often small and the depth of field is limited, axis lighting can help in uniformly lighting the tiny subjects. This is important to bring out intricate details and textures without casts by shadows which might otherwise overshadow critical aspects of the subject.
Practical Tips to Master Axis Lighting
1. Use of Light Modifiers:
Although axis lighting can inherently reduce shadows, the light source itself can still be harsh or overly bright. Utilizing light modifiers such as softboxes, diffusers, or ring lights can help in softening the light and creating a more pleasing visual outcome. Ring lights, in particular, are popular in beauty and macro photography due to their ability to provide even, on-axis illumination with minimal effort.
2. Balancing Exposure:
Since axis lighting tends to highlight all parts of the subject equally, it is important to carefully balance the exposure. Overexposure can result in loss of detail while underexposure might fail to bring out the desired evenness. Using a light meter or relying on the camera’s histogram can assist in achieving the right exposure balance.
3. Creating Depth with Background Light:
One of the drawbacks of axis lighting is the potential for images to appear flat. To counter this, photographers can introduce additional light sources focused on the background. This separation light can add depth and a three-dimensional feel to the image, making the subject stand out more prominently.
4. Integrated Post-Processing:
Post-processing software can serve as an invaluable tool to enhance images shot with axis lighting. Techniques like dodging and burning can accentuate certain areas, adding a sense of depth and dimension. Moreover, adjustments in contrast and clarity can refine the overall feel of the image.
5. Combining with Other Lighting Techniques:
Axis lighting does not have to exist in isolation. Combining it with other lighting techniques such as side lighting or backlighting can yield more dynamic results. For instance, while the main light source can be on-axis to illuminate the face evenly, a secondary side light can add shadows and depth, producing a more artistic effect.
Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
- Even Lighting: The primary advantage of axis lighting is the even distribution of light across the subject, which can be ideal for reducing shadows and highlighting details.
- Simplicity: It is a straightforward setup that doesn't require complex arrangements and is particularly useful for beginners.
- Versatility: Axis lighting can be versatile in applications ranging from portraits to product photography, making it a go-to technique in various scenarios.
Challenges:
- Risk of Flatness: Without shadows, images can lack depth and dimensionality. It is crucial for photographers to find ways to reintroduce a sense of depth either through additional lighting or post-processing.
- Potential for Harshness: Direct lighting can sometimes result in harsh highlights and reflections, particularly on shiny or reflective surfaces. Using diffusers or other light modifiers is essential to mitigate these effects.
Final Thoughts
Axis lighting is a powerful technique in the photographer's arsenal, offering the ability to achieve clear, evenly lit images that are free from distracting shadows. Whether you're capturing the delicate details of a product, the intricate textures in a macro shot, or the flawless complexion in a portrait, on-axis lighting provides a reliable and effective solution. However, like any technique, it requires a thoughtful approach to mitigate its limitations and enhance its strengths. By mastering the principles of axis lighting and integrating it with other lighting methods, photographers can elevate their work, ensuring that their images convey the desired impact and aesthetic.
In conclusion, the mastery of axis lighting opens a world of possibilities for photographers. It allows for the creation of images that are not only technically proficient but also visually captivating. So, experiment with axis lighting, understand its nuances, and watch as your photographic creations come to life with impeccable clarity and evenness.

































There are no comments for this blog.