What Is Night Vision Surveillance Cameras?
Night vision surveillance cameras are essential tools for modern security systems, providing continuous monitoring in low-light or completely dark environments. They use advanced technologies to ensure that properties, buildings, and public spaces are secure around the clock, not just during the day. Whether you’re installing a security system for your home, business, or a larger facility, understanding the functionality, benefits, and types of night vision surveillance cameras is crucial to making the right choice.
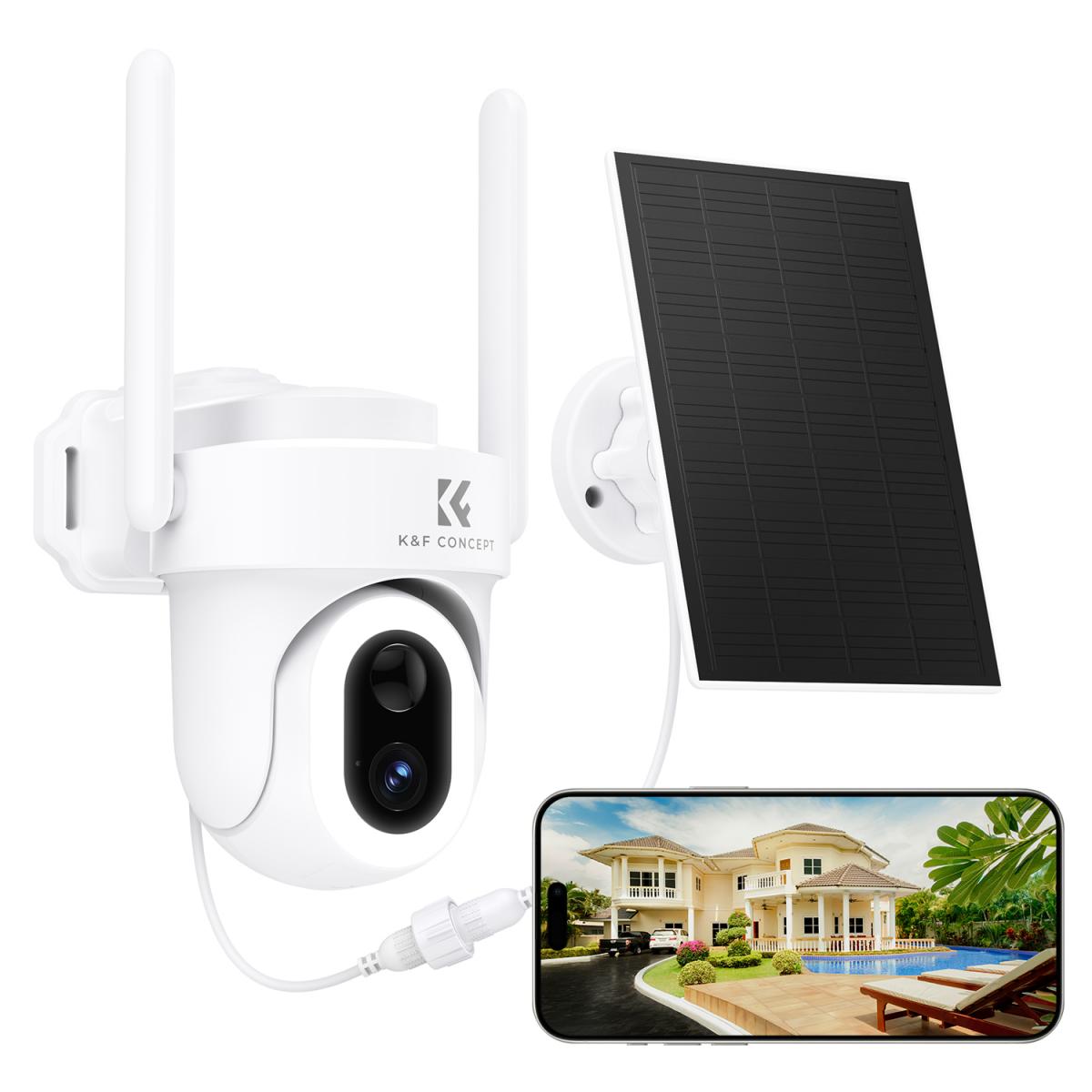

In this article, we will explore the concept of night vision cameras, how they work, the different technologies they use, and practical considerations for selecting the best one for your needs.
What are Night Vision Surveillance Cameras?
Night vision surveillance cameras are designed to capture video footage in environments with minimal to no lighting. Unlike traditional cameras that rely on visible light, night vision cameras use infrared (IR) light or thermal imaging to see in the dark. The video footage is either visible in grayscale or in full color, depending on the technology employed. These cameras are particularly valuable for monitoring areas at night, or in places where natural light or artificial lighting is insufficient, like warehouses, parking lots, or even private homes.
How Do Night Vision Surveillance Cameras Work?
Night vision cameras function using various technologies, depending on the type of camera. The most common technologies include infrared (IR) vision and thermal imaging. Let's break down how each works:
1. Infrared Night Vision (IR) Cameras
Infrared night vision cameras use IR LEDs to illuminate the surroundings with infrared light, which is invisible to the human eye. These cameras can pick up this infrared light and convert it into visible footage. The illumination provided by IR LEDs is usually sufficient for the camera to "see" objects up to a certain distance, depending on the camera's specifications.
The working principle of infrared cameras can be summarized as follows:
- IR LEDs emit infrared light: The camera’s LEDs emit infrared light in a pattern around the camera's lens. This light is not visible to humans but is picked up by the camera's sensors.
- The camera captures the reflected infrared light: When objects in the field of view reflect this IR light, the camera’s sensor captures the reflection, even in total darkness.
- The image is displayed in black and white or grayscale: Since the light captured is infrared, the footage is usually displayed in monochrome or black and white, making it easier for the camera to process the images.
IR cameras have a certain range of night vision, which is often referred to as the IR range. This range can vary depending on the camera model, with some cameras offering a range of just 30 feet, while others can cover up to 200 feet or more.
2. Thermal Imaging Cameras
Unlike infrared cameras, thermal imaging cameras do not rely on infrared light for illumination. Instead, they detect the heat emitted by objects. Every object, whether it's living or non-living, emits infrared radiation as heat, even in total darkness. Thermal imaging cameras can pick up these heat signatures and display them as different shades of color, often from red to blue.
The benefits of thermal imaging cameras include:
- Visibility in complete darkness: Since thermal cameras don't need external light sources, they can function in complete darkness, detecting heat from people, animals, or machinery.
- Enhanced object identification: Thermal cameras make it easier to identify living beings, vehicles, or other heat-emitting objects, even through fog, smoke, or other environmental factors that could obscure visible light.
However, thermal cameras are usually more expensive than infrared cameras due to the complexity of the technology. They are ideal for high-security areas, such as military or industrial sites, where detecting heat sources is critical.
Types of Night Vision Surveillance Cameras
Night vision surveillance cameras come in various types, each designed to meet specific security needs. The primary types include:
1. Analog Night Vision Cameras
Analog cameras are the traditional type of CCTV camera and work by transmitting analog signals to a recording device (like a DVR). These cameras are cost-effective and commonly used for basic security setups. However, they may offer lower resolution compared to their digital counterparts and have limited night vision capabilities.
Advantages:
- Affordable and easy to install.
- Suitable for small-scale or low-budget security setups.
Disadvantages:
- Lower resolution compared to IP cameras.
- Less scalable and harder to upgrade.
2. IP Night Vision Cameras
Internet Protocol (IP) cameras are more advanced and use a network connection to transmit video data. These cameras can transmit high-definition video and allow for remote monitoring through smartphones, tablets, or computers. IP cameras typically offer better image quality, more advanced features (like motion detection and smart alerts), and can integrate with other security systems.
Advantages:
- High-resolution video quality, often in HD or 4K.
- Remote access for monitoring from anywhere.
- Easier to expand and upgrade with modern features.
Disadvantages:
- Requires a stable and fast internet connection.
- Higher cost compared to analog cameras.
3. Wireless Night Vision Cameras
Wireless night vision cameras connect to the internet via Wi-Fi, making them an attractive option for home security or areas where running cables is difficult or impractical. These cameras are simple to install and can be controlled through mobile apps or cloud-based systems.
Advantages:
- Easy to install with no need for complex wiring.
- Can be controlled remotely via apps.
- Portable and flexible.
Disadvantages:
- Dependent on a reliable Wi-Fi connection.
- Possible signal interference issues in some environments.
4. PTZ Night Vision Cameras
Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) cameras are designed for larger areas, such as parking lots or open spaces, where a fixed camera might miss important details. These cameras can be remotely controlled to pan, tilt, and zoom, offering full control over what part of the scene is being monitored.
Advantages:
- Can cover large areas with remote movement.
- Provides better flexibility for monitoring different zones.
Disadvantages:
- Typically more expensive.
- More complex to install and maintain.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Night Vision Surveillance Camera
When selecting a night vision surveillance camera, several factors should be taken into account to ensure it meets your specific needs. Here are the most important factors to consider:
1. Resolution and Image Quality
Resolution is one of the most critical aspects of a surveillance camera. Higher resolution cameras provide clearer images, which can be crucial in identifying individuals or objects. Cameras with resolutions of at least 1080p (Full HD) are recommended for most applications. For high-security environments, 4K cameras might be preferred for their ultra-sharp image quality.
2. Night Vision Range
Consider how far the night vision can reach. If you need to monitor a wide area, such as a yard or parking lot, choose a camera with a longer IR range. Typically, night vision cameras can offer ranges anywhere from 30 feet to over 200 feet. Cameras with a higher IR range are ideal for larger properties.
3. Field of View (FOV)
The field of view refers to the area the camera can cover. A camera with a wider FOV will capture more of the area, reducing the need for additional cameras. For larger areas, PTZ cameras may offer the flexibility to adjust the view.
4. Power Source and Connectivity
Choose a camera with a power source and connectivity that fits your installation environment. Wired cameras typically provide more reliable and uninterrupted power, while wireless cameras offer more flexibility. For wireless cameras, ensure that your Wi-Fi network can support them, especially if they transmit high-definition footage.
5. Weather Resistance and Durability
For outdoor installations, ensure that the camera is weatherproof. Look for cameras with an IP rating of at least IP66 (dust-tight and able to withstand heavy rain) to ensure they can handle different weather conditions.
6. Integration with Other Security Systems
Many modern surveillance cameras can integrate with alarm systems, smart home devices, or other security solutions. If you already have a security system, check for compatibility to create a unified security network.
Conclusion
Night vision surveillance cameras are indispensable in modern security systems. Whether you opt for infrared or thermal imaging technology, these cameras provide the critical functionality needed to protect your property during the night or in low-light conditions. When choosing a camera, consider factors like resolution, night vision range, and field of view to ensure you select a model that fits your specific needs. By understanding how these cameras work and the different types available, you can make an informed decision that enhances the security and safety of your home or business.






































There are no comments for this blog.