What Lens Filter Should I Buy?
When it comes to photography, the choice of lens filters can significantly impact the quality and creativity of your images. Whether you are a professional photographer or an enthusiastic hobbyist, understanding the different types of lens filters and their specific uses is crucial. This article will guide you through the various types of lens filters, their purposes, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Understanding Lens Filters

Lens filters are accessories that attach to the front of your camera lens. They serve various purposes, from protecting the lens to enhancing image quality and adding creative effects. Here are the main types of lens filters you should consider:
1. UV Filters
2. Polarizing Filters
3. Neutral Density (ND) Filters
4. Graduated Neutral Density (GND) Filters
5. Color Filters
6. Special Effects Filters
UV Filters

Purpose: UV filters are primarily used to protect the lens from dust, scratches, and moisture. They also reduce the haziness caused by ultraviolet light, which can be more noticeable at high altitudes or in very sunny conditions.
When to Use: UV filters are ideal for everyday use. They are particularly useful in outdoor photography where the lens is exposed to the elements.
Pros:
- Protects the lens
- Reduces UV haze
- Minimal impact on image quality
Cons:
- Some argue they are unnecessary with modern lenses that already have UV protection
Polarizing Filters

Purpose: Polarizing filters reduce reflections and glare from non-metallic surfaces like water and glass. They also enhance the colors and contrast in your images, making skies appear bluer and foliage greener.
When to Use: Polarizing filters are perfect for landscape photography, especially when shooting water bodies, skies, or through glass.
Pros:
- Reduces reflections and glare
- Enhances color saturation and contrast
- Can make skies appear more dramatic
Cons:
- Reduces the amount of light entering the lens, requiring longer exposure times
- Can be expensive
Neutral Density (ND) Filters

Purpose: ND filters reduce the amount of light entering the lens without affecting the color of the image. This allows for longer exposure times or wider apertures in bright conditions.
When to Use: ND filters are essential for long-exposure photography, such as capturing smooth water effects, motion blur in clouds, or achieving a shallow depth of field in bright light.
Pros:
- Enables long exposures in bright light
- Allows for wider apertures
- Versatile for various creative effects
Cons:
- Requires careful handling to avoid vignetting
- Can be costly
Graduated Neutral Density (GND) Filters
Purpose: GND filters are similar to ND filters but with a gradient transition from dark to clear. They are used to balance the exposure between the sky and the foreground in landscape photography.
When to Use: GND filters are ideal for sunrise and sunset photography, where the sky is much brighter than the foreground.
Pros:
- Balances exposure in high-contrast scenes
- Enhances landscape photography
Cons:
- Requires precise positioning
- Limited to specific scenarios
Color Filters
Purpose: Color filters alter the color balance of your images. They can be used to correct color casts or to add creative effects.
When to Use: Color filters are often used in black and white photography to enhance contrast. They can also be used in color photography for creative effects.
Pros:
- Enhances contrast in black and white photography
- Adds creative color effects
Cons:
- Limited use in digital photography due to post-processing capabilities
- Can be challenging to use effectively
Special Effects Filters
Purpose: Special effects filters include a variety of filters designed to create unique effects, such as starbursts, soft focus, or infrared.
When to Use: These filters are used for creative photography to achieve specific artistic effects.
Pros:
- Adds unique effects to images
- Expands creative possibilities
Cons:
- Niche use cases
- Effects can often be replicated in post-processing
Choosing the Right Filter
When deciding which lens filter to buy, consider the following factors:
1. Purpose: Determine what you want to achieve with the filter. Are you looking to protect your lens, enhance colors, reduce reflections, or create special effects?
2. Type of Photography: Your photography style will influence your choice. Landscape photographers might prioritize polarizing and ND filters, while portrait photographers might focus on UV and special effects filters.
3. Budget: Filters can range from affordable to quite expensive. Set a budget and prioritize the filters that will have the most impact on your photography.
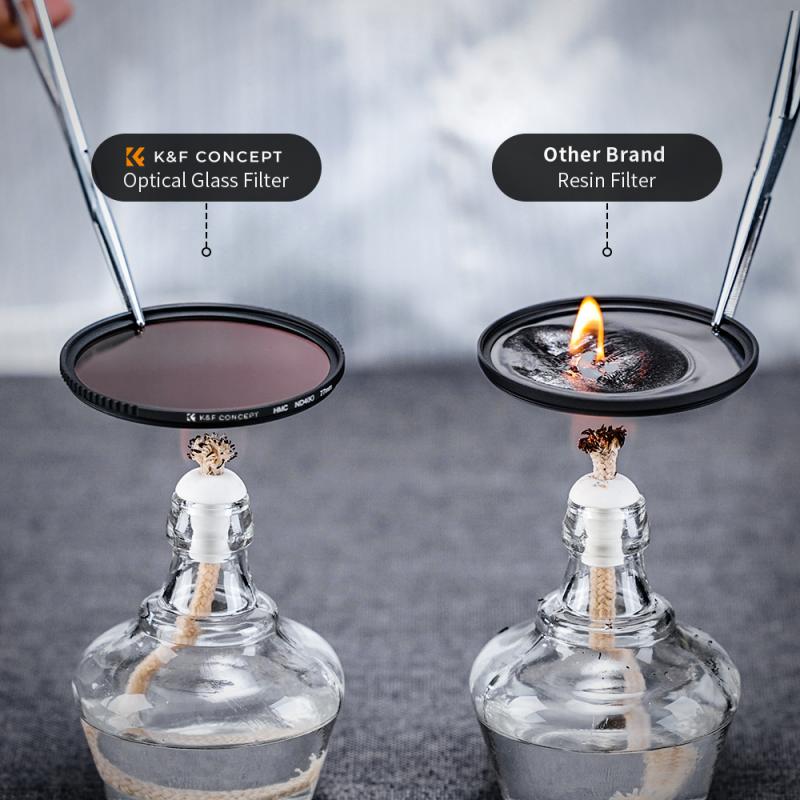
4. Quality: Invest in high-quality filters from reputable brands. Cheap filters can degrade image quality and introduce unwanted artifacts.
5. Compatibility: Ensure the filter size matches your lens. Filters come in various diameters, so check your lens specifications before purchasing.
Practical Tips for Using Filters
1. Stacking Filters: Avoid stacking multiple filters as it can cause vignetting and reduce image quality. If you need multiple effects, consider using a filter holder system.
2. Cleaning: Keep your filters clean to avoid smudges and dust spots. Use a microfiber cloth and lens cleaning solution.
3. Storage: Store your filters in a protective case to prevent scratches and damage.
4. Experiment: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different filters and techniques. Photography is an art, and filters can help you explore new creative possibilities.
Choosing the right lens filter can significantly enhance your photography, whether you are looking to protect your lens, reduce reflections, balance exposures, or add creative effects. By understanding the different types of filters and their specific uses, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your photography goals. Remember to consider your purpose, photography style, budget, and filter quality when making your choice. With the right filters in your kit, you can elevate your photography to new heights and capture stunning images that stand out.

































There are no comments for this blog.