What To Look For In A Telescope?
When it comes to choosing a telescope, the process can be both exciting and overwhelming. With a myriad of options available, each boasting different features and specifications, it's crucial to understand what to look for to ensure you make an informed decision. Whether you're a beginner stargazer or an experienced astronomer, selecting the right telescope can significantly enhance your celestial observations. In this article, we will delve into the key factors to consider when purchasing a telescope, helping you navigate through the technical jargon and make a choice that aligns with your needs and interests.
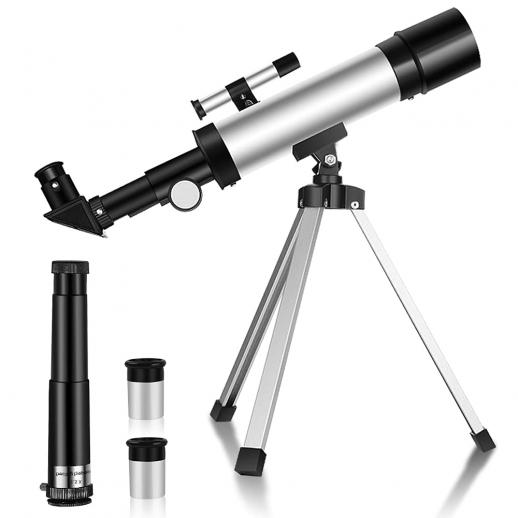

1. Aperture: The Heart of the Telescope
The aperture is arguably the most critical feature of a telescope. It refers to the diameter of the telescope's main optical component, which can be either a lens or a mirror. The aperture determines the amount of light the telescope can gather, directly impacting the clarity and brightness of the images you observe. A larger aperture allows you to see fainter objects and finer details.
For beginners, a telescope with an aperture of at least 70mm (2.8 inches) is recommended. Intermediate users might look for apertures in the range of 100mm (4 inches) to 200mm (8 inches). Advanced astronomers often prefer telescopes with apertures larger than 200mm. However, it's essential to balance aperture size with other factors like portability and budget.
2. Focal Length and Focal Ratio: Understanding Magnification
The focal length of a telescope is the distance between the main optical component and the point where the telescope forms an image. It plays a significant role in determining the magnification power of the telescope. The focal ratio (f/number) is the focal length divided by the aperture. A lower focal ratio (f/5 or lower) indicates a wider field of view, which is ideal for observing large celestial objects like galaxies and nebulae. A higher focal ratio (f/10 or higher) provides higher magnification, suitable for viewing planets and the moon.
When choosing a telescope, consider what you primarily want to observe. For deep-sky objects, a telescope with a lower focal ratio is preferable. For planetary observation, a higher focal ratio is beneficial.
3. Mount Types: Stability and Ease of Use
The mount is the structure that supports the telescope and allows it to move. There are two main types of mounts: altazimuth and equatorial.
- Altazimuth Mounts: These are simple and intuitive, moving up-down (altitude) and left-right (azimuth). They are ideal for beginners due to their ease of use and quick setup. However, they are less suitable for long-exposure astrophotography.
- Equatorial Mounts: These are more complex and designed to follow the rotation of the Earth, making them ideal for tracking celestial objects over time. They are essential for astrophotography and more advanced observations but require a steeper learning curve.
Choosing the right mount depends on your experience level and whether you plan to engage in astrophotography.
4. Optical Design: Reflectors, Refractors, and Compound Telescopes
Telescopes come in three primary optical designs: refractors, reflectors, and compound (catadioptric) telescopes.
- Refractors: These use lenses to gather and focus light. They are known for their sharp and high-contrast images, making them excellent for planetary and lunar observations. However, they can be more expensive per inch of aperture and are prone to chromatic aberration (color fringing).
- Reflectors: These use mirrors to gather and focus light. They offer more aperture for the money and are free from chromatic aberration. Reflectors are great for deep-sky observations but require regular maintenance, such as mirror alignment (collimation).
- Compound Telescopes: These combine lenses and mirrors to offer a compact design with versatile performance. They are excellent all-rounders, suitable for both planetary and deep-sky observations. However, they can be more expensive and heavier than other types.
Your choice of optical design should align with your observational interests and budget.
5. Portability: Observing on the Go
Portability is an essential factor, especially if you plan to transport your telescope to different observation sites. Smaller telescopes are easier to carry and set up but may have limited capabilities. Larger telescopes offer better performance but can be cumbersome to move.
Consider how often you will need to transport your telescope and choose a model that balances performance with portability. For urban dwellers with limited storage space, a compact and lightweight telescope is ideal.
6. Accessories: Enhancing Your Observing Experience
A telescope's performance can be significantly enhanced with the right accessories. Some essential accessories to consider include:
- Eyepieces: Different eyepieces provide varying magnifications. A good telescope should come with at least two eyepieces, but investing in additional high-quality eyepieces can enhance your viewing experience.
- Finderscopes: These small scopes attached to the main telescope help you locate objects in the sky. Red-dot finders and optical finderscopes are common options.
- Barlow Lenses: These lenses increase the magnification of your eyepieces, effectively doubling or tripling their power.
- Filters: Filters can enhance the visibility of certain celestial objects. For example, moon filters reduce glare, while light pollution filters improve contrast in urban areas.
7. Budget: Balancing Cost and Quality
Telescopes come in a wide range of prices, from affordable beginner models to high-end professional instruments. It's essential to set a budget and understand what features are most important to you. While it's tempting to go for the cheapest option, investing in a quality telescope can provide a more enjoyable and long-lasting experience.
8. Brand Reputation and Reviews
Finally, consider the reputation of the brand and read reviews from other users. Established brands like Celestron, Meade, and Orion have a track record of producing reliable and high-quality telescopes. User reviews can provide valuable insights into the performance and durability of a telescope.
Choosing the right telescope involves considering various factors, including aperture, focal length, mount type, optical design, portability, accessories, budget, and brand reputation. By understanding these elements, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your observational goals and enhances your stargazing experience. Whether you're exploring the craters of the moon, the rings of Saturn, or distant galaxies, the right telescope can open up a universe of possibilities. Happy stargazing!